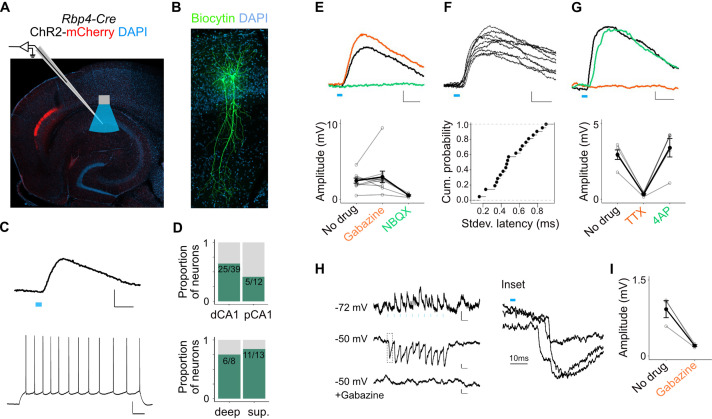
Figure 5. L5a neurons of the medial entorhinal cortex (MEC) provide direct excitatory and indirect inhibitory inputs to pyramidal cells in CA1.
(A) Experimental design showing viral expression, placement of patch-clamp electrode, and light delivery over CA1. (B) Examples of biocytin filled pyramidal neurons recorded in CA1. (C) An example electrical recording of a pyramidal neuron at rest (−67 mV) showing depolarizing responses upon 3-ms light stimulation (top) (blue line, scale bar: 1 mV, 10 ms). Train of action potentials upon 200 pA step-current injection (bottom; scale bar: 20 mV, 100 ms). (D) Proportion of responsive pyramidal neurons located in the distal and proximal halves of CA1 (top). The difference in proportions was not significant (X-squared = 1.9071, df = 1, p value = 0.167291, chi-squared test, n = 12 cells in proximal and n = 39 cells in distal CA1). Proportion of responsive pyramidal neurons located in the deep versus superficial locations of CA1 pyramidal cell layer (bottom) (X-squared = 0.2969, df = 1, p value = 0.585804, chi-squared test, n = 8 cells in deep SP and n = 13 cells in superficial SP). (E) Effects of bath application of Gabazine (orange, n = 10 cells, 9 mice) and NBQX (green, n = 5 cells) on postsynaptic potentials (PSPs) recorded from a pyramidal neuron (scale bar: 0.5 mV, 10 ms) and a summary plot of PSP amplitude measurements for all tested pyramidal neurons. Note that some neurons were only treated with Gabazine which did not cause a significant change in amplitudes (p = 0.97, two-tailed Student’s t-test, n = 10 cells, 9 mice). (F) An example of ten consecutive PSP responses recorded from a single pyramidal neuron illustrates the short and invariant latency of PSPs (scale bar: 0.5 mV, 10 ms) and a cumulative probability plot of standard deviation of latencies for neurons with PSP responses that were >1 mV in amplitude (n = 20 cells). (G) Effects of bath application of tetrodotoxin (TTX; orange) and 4-aminopyridine (4-AP; green) on PSPs recorded from a pyramidal neuron (scale bar: 0.5 mV, 10 ms) and a summary plot of changes in PSP amplitudes for all tested pyramidal neurons. TTX application abolished responses (n = 5 cells, 5 mice, p = 0.01, two-tailed Student’s t-test). (H, I) An example inhibitory PSP response recorded from a pyramidal neuron upon 10 Hz light stimulation (blue bars). Response polarity reversed when the neuron’s membrane potential was adjusted to –50 mV and was abolished after application of Gabazine (scale bars: 0.2 mV, 100 ms). Inset shows the long latency (>10 ms) of PSP onset indicating polysynaptic connectivity.