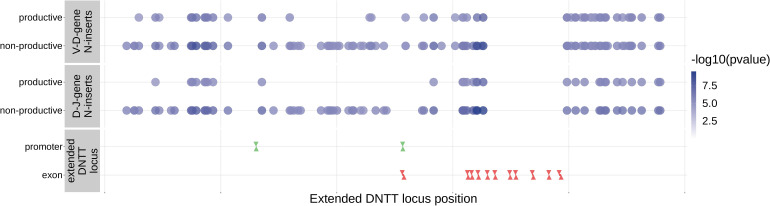
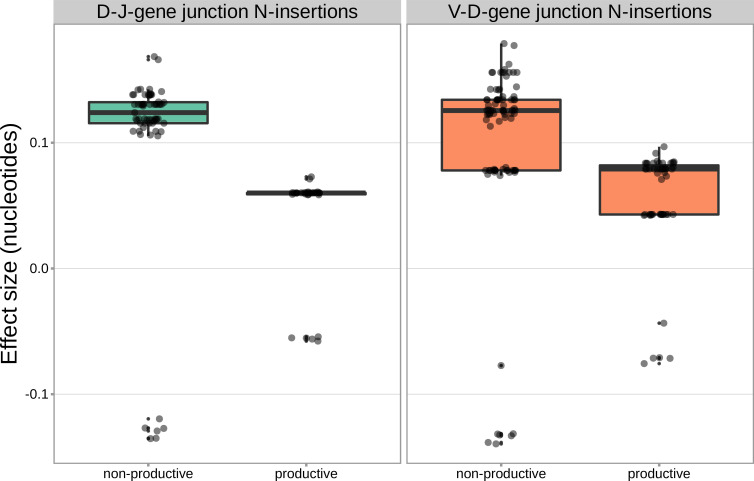
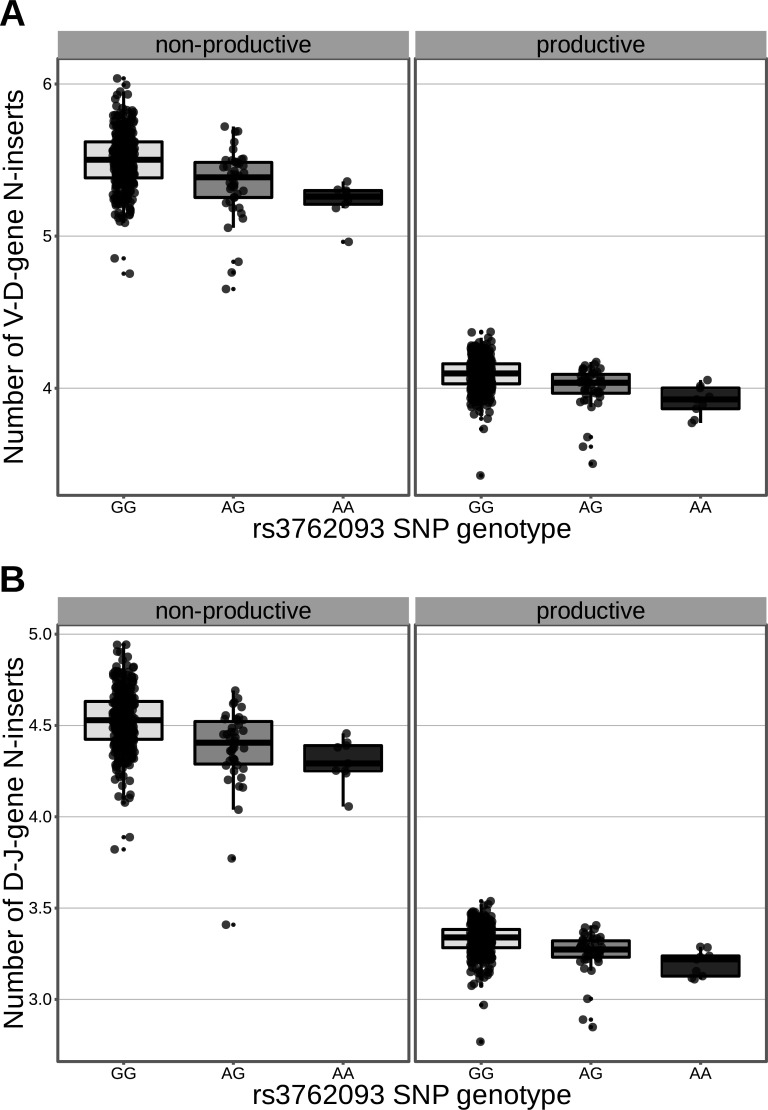
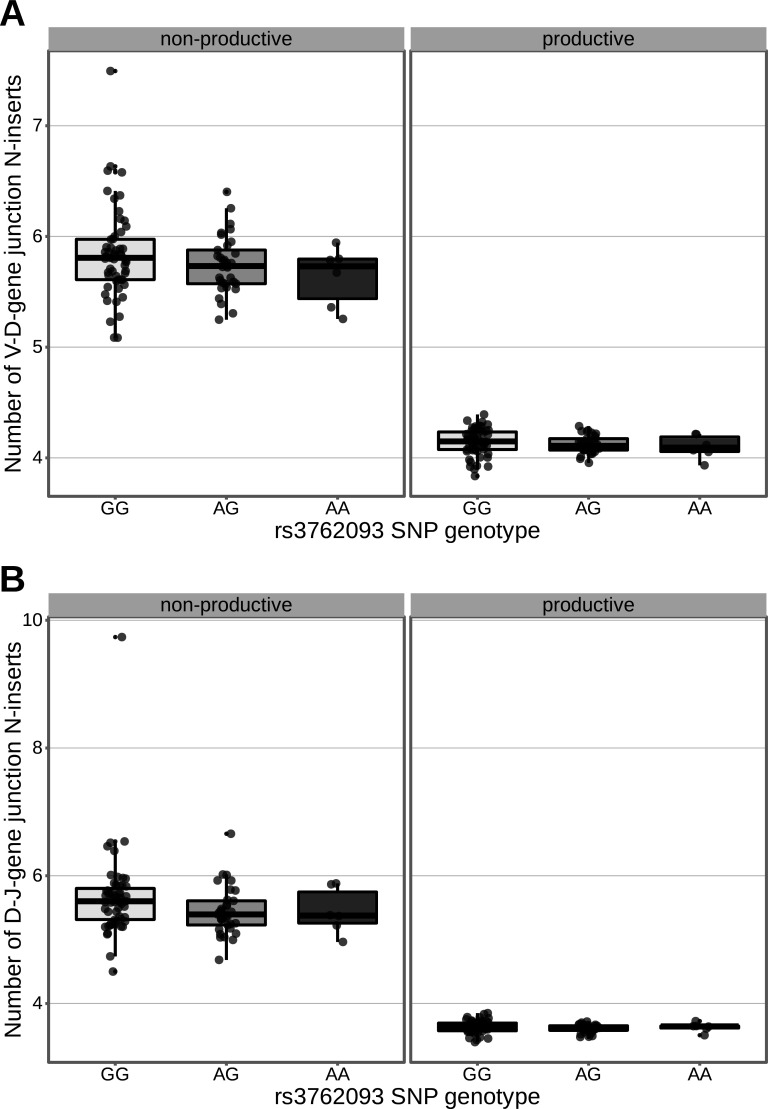
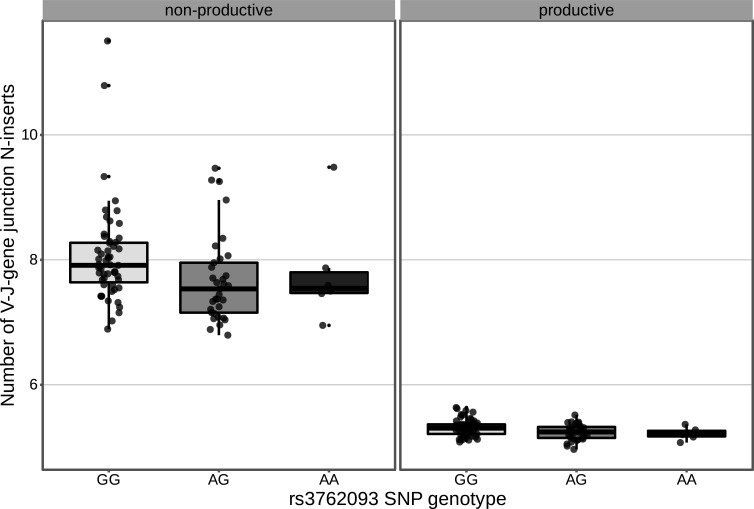
Figure 6. Within the DNTT locus, many of the significant SNP associations overlapped between N-insertion types when using DNTT gene-level Bonferroni-corrected p-value significance threshold of .
Downward arrows represent promoter/exon starting positions and upward arrows represent promoter/exon ending positions.