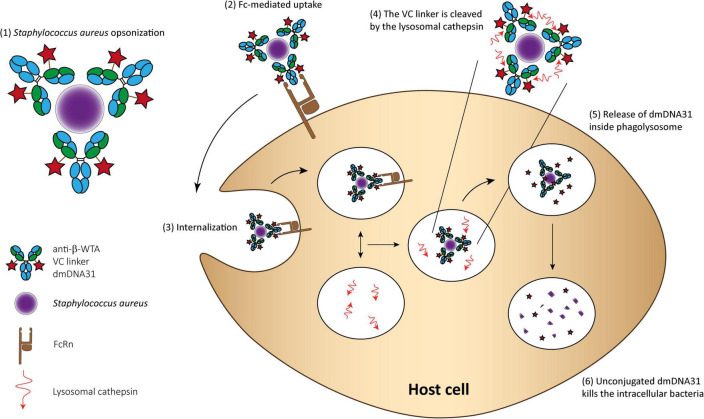
FIGURE 3.
THIOMAB™ AAC mechanism of action for killing Staphylococcus aureus. (1) The AAC binds Staphylococcus aureus bacteria; (2) The Fc domain of the monoclonal antibody is recognized by the FcRn on the surface of professional phagocytes or other host cells, such as epithelial cells; (3) The complex is internalized; (4) Fusion between the phagosome and lysosome and cleavage of the VC linker; (5) The active dmDNA31 is released attacking the intracellular bacteria; and (6) Unconjugated dmDNA31 eliminates the intracellular bacteria.