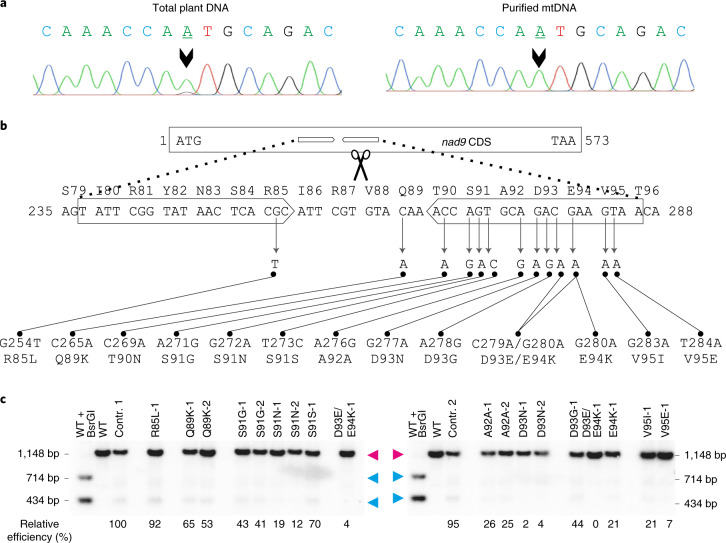
Fig. 3. Apparent heterochondriomy, locations of the TALEN-induced point mutations in nad9 and effects of the point mutations on TALEN cleavage activity.
a, Genotyping of an S91N-1 mutant plant carrying the G272A mutation. Sequencing of PCR products amplified from total plant DNA (with primers oJF271 and oJF272; Supplementary Table 2) suggested persistent heteroplasmy (that is, the presence of residual copies of wild-type nad9 alleles), as evidenced by an A + G double peak (arrowhead, left sequence). However, when the same PCR product was generated from purified mtDNA as a template, a clean single A peak is seen (right sequence). The sequencing was done with primer oJF271. b, Overview of all TALEN-induced mutations obtained in nad9. The nucleotide positions in the nad9 coding sequence (ATG = 1) and the amino acid positions in the Nad9 protein are given. The block arrows denote the pJF1006 TALEN binding sites. The ‘left’ (HA-)TALEN (not present in line Nt-JF1006-30) extends from nucleotide positions 237 to 255 and the ‘right’ (FLAG-)TALEN from positions 268 to 286. The scissors point to the predicted TALEN cut site. c, Analysis of TALEN cleavage activity by Southern blotting using pools of kanamycin-resistant seedlings (from back-crosses of the original mutants with the wild type). The same restriction enzymes and hybridization probe as in Fig. 1b were used, but electrophoretic separation was done in a 2% agarose gel. To determine the relative cutting efficiencies, the percentage of cut nad9 was calculated for each lane and then divided by the respective value for control line 1 (contr. 1). The smaller of the two nad9 cleavage products was used for quantification, because it is covered by a larger portion of the hybridization probe. Contr. 1 and contr. 2 are descendants of Nt-JF1006-30 plants having gone through the same mutagenesis procedure as the point mutants, but retaining a wild-type nad9 sequence. Line D93E/E94K-1 is represented twice (descendants of two different vegetative clones of the original mutant plant). The full Southern blot with enhanced contrast settings is presented in Extended Data Fig. 5. Unlike all other mutants, line R85L-1 may not be the result of a gene drive effect. A technical replicate of the Southern blot yielded similar results.