Figure 6.
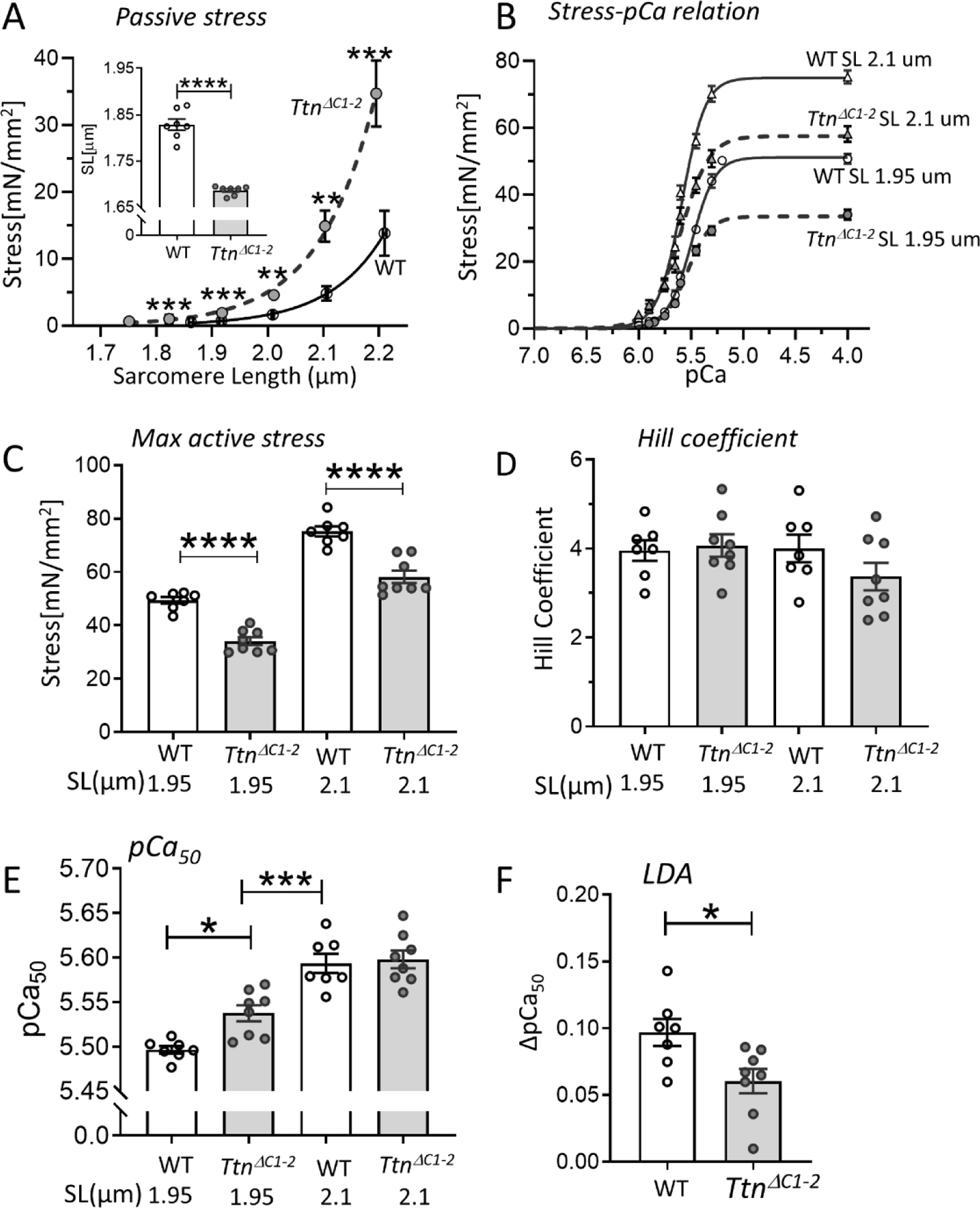
Myofilament Ca2+ sensitivity and length dependence of activation (LDA). (A) Passive stress-SL relation of skinned LV myocardium of WT and TtnΔC1−2 shows a higher passive stress and a shorter slack SL (inset) in TtnΔC1−2 mice. B) Average stress-pCa curves at SL 1.95 µm and 2.1 µm for both genotypes. C) The maximal active stress is lower in TtnΔC1−2 at both SLs. D) The Hill coefficient (nH), which reflects cooperative activation is not different. E) The pCa50, which reflects the myofilament Ca2+ sensitivity, is increased in TtnΔC1−2 at SL 1.95 µm but is not different at 2.1 µm. The pCa50 of TtnΔC1−2 at SL 1.95 um is lower than WT at SL 2.1 um. F) The LDA as reflected by the pCa50 2.1 µm – pCa50 1.95 µm is reduced in TtnΔC1–2. n=7–8 mice per group, 2 preparations per mouse. Each data point represents the mean value of all muscle preparations from a single mouse. Mean ± S.E.M are shown in the bar graphs. Mann-Whitney test for A and F, Two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test for C-E: *P < 0.05 ***P < 0.001 ****P < 0.0001.
