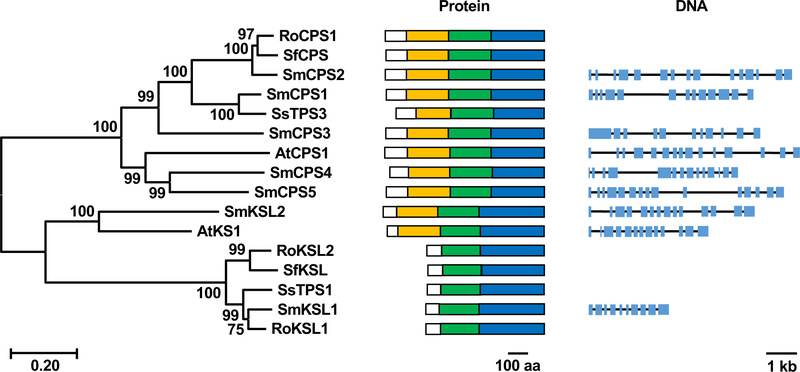
Figure 5. Phylogeny, protein and genomic structure of CPS and KSL genes in S. miltiorrhiza.
Left) Phylogenetic tree of diterpene cyclases and synthases from Salvia miltiorrhiza (Sm), Salvia splendens (Ss), Salvia fruticosa (Sf), Rosemarinus officinalis (Ro) and Arabidopsis thaliana (At), constructed using the neighbor-joining method with MEGA-X. Numbers at nodes indicate bootstrap values (percentage of 1000 replicates). The scale bar at bottom represents the genetic distance. Middle) Domain architecture (box coloring: white, plastid targeting sequence; orange, γ domain; green, β domain; blue, α domain). Right) Exon/intron structure of the indicated genes. Blue boxes indicate exons and black lines indicate introns