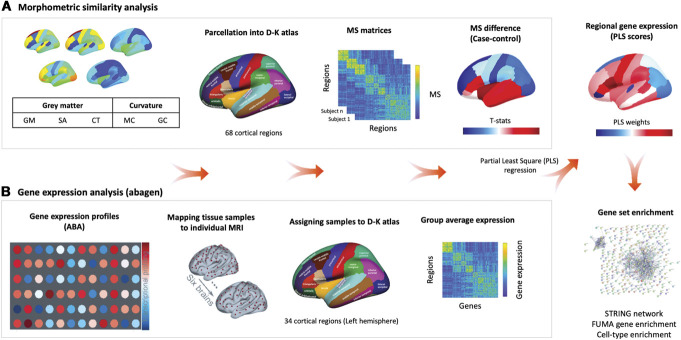
Figure 1.
Overview of the analysis pipeline. (A) Morphometric similarity (MS) analysis. We constructed individual cortical MS matrices using 5 structural magnetic resonance imaging features (eg, gray matter volume [GM], surface area [SA], cortical thickness [CT], mean curvature [MC], and Gaussian curvature [GC]) extracted from 68 cortical regions of the Desikan–Killiany (DK) Atlas. For each individual, we produced a 68 × 68 MS matrix by correlating the normalized (z-scores) values of the 5 structural features between each pair of regions in the atlas. For each region, we averaged across all the edges involving that area to obtain a singular representation of the mean MS score for that region. We then computed case–control differences for each region, while accounting for age, gender, and total intracranial volume. (B) Gene expression analysis. We used abagen to obtain gene expression profiles from the Allen Human Brain Atlas (AHBA) in 68 regions (left hemisphere only) across the 6 postmortem brains sampled in this atlas. We excluded all genes with normalized expression values below the background (15,633 genes met this criterion). When more than one probe was available for a certain gene, we selected the probe with higher consistency in expression across the 6 donors. We used partial least squares regression (PLS) to rank all genes according to their association with the case–control changes in MS. Finally, we performed a set of enrichment analyses on the top genes positively or negatively associated with case–control differences in MS.