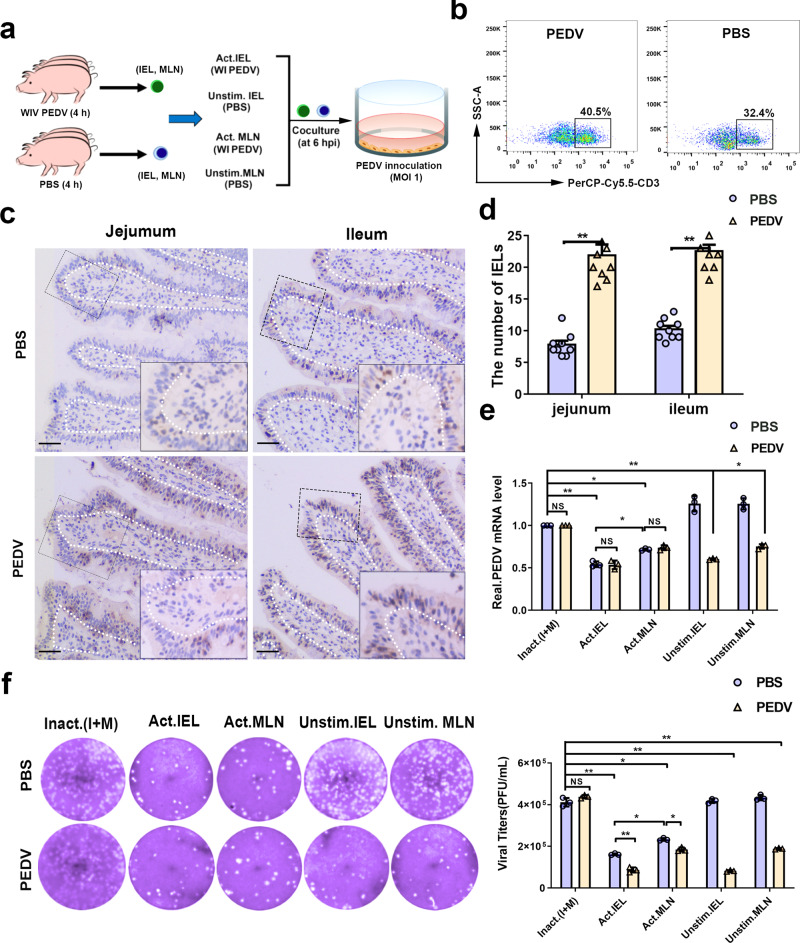
Fig. 6. Oral inoculation with porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) pre-activated intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs) and increased their antiviral activity against virus infection.
a For in vivo IELs activation experiment, piglets were sacrificed 4 h after PEDV inoculation, n = 3 piglets per group. The scheme depicts that intestinal IELs isolated from piglets orally inoculated with PEDV (PBS inoculation was used as a negative control) were pretreated with whole inactivated PEDV for pre-activation (DMEM medium was used as a negative control) and then co-cultured with PEDV-infected epithelial cells for 24 h. b The percentage of CD3-positive IELs in the jejunum of piglets were analyzed using fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS). c Immunohistochemistry (IHC) analysis displayed the distribution pattern of IELs influenced by PEDV inoculation. Scale bars, 10 μm. d The numbers of IELs shown in (c) were quantified and displayed on a histogram. e The PEDV RNA expression in epithelial cells from the co-culture system in (a) was quantitated using RT-qPCR. f Moreover, the infectious viral particles in the culture medium of the coculture system in (a) were detected by plaque formation. The histogram summarizes the plaque assay results. All data are the mean ± SD, and comparisons were performed using one-way ANOVA. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. The results are from at least three different experiments.