Fig. 4. The effect of neuraminidase (NA) inhibition on IAV diffusion through and adhesion to human mucus.
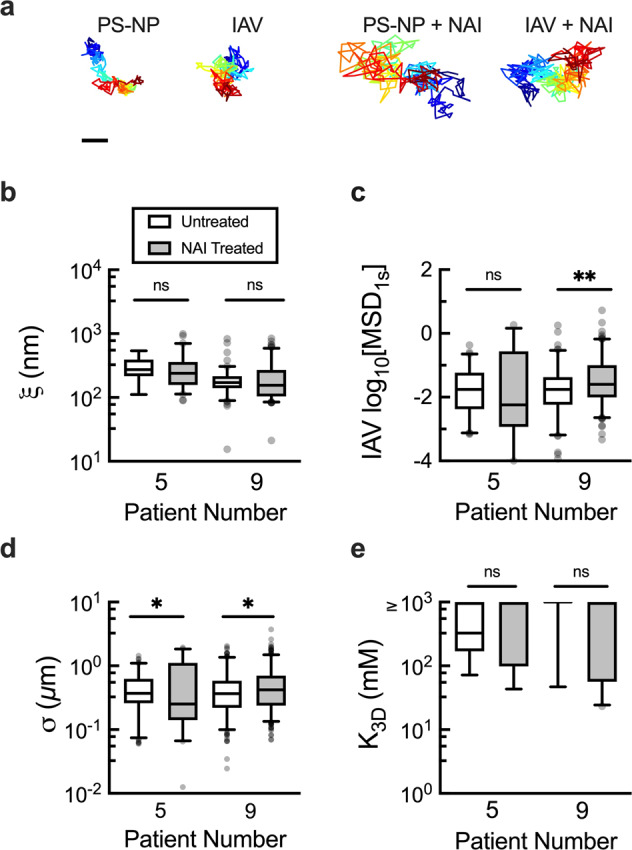
a Representative trajectories of PS-NP and IAV untreated and treated with NAI in human mucus. Scale bar = 0.2 µm. b Calculated pore size (ξ) in untreated (white) and NA inhibitor (NAI) treated (zanamivir; 10 µM final concentration; grey) based on PS-NP diffusion in human mucus. c Measured log10MSD1s for IAV diffusion in untreated and NAI treated human mucus. Box and whisker plots of d average trajectory diameter (σ) and e calculated dissociation constants (K3D) with and without NAI treatment. IAV with a calculated K3D ≥ 1000 mM are compiled with these high K3D indicative of negligible IAV-mucus interactions. Whiskers are drawn down to the 5th percentile, up to the 95th percentile, and outliers are plotted as points. Data sets (n = 2 patient samples) statistically analyzed with two-tailed Mann-Whitney test: ns = not significant; p > 0.05, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. Patient numbers correspond with those in Figs. 2 and 3.
