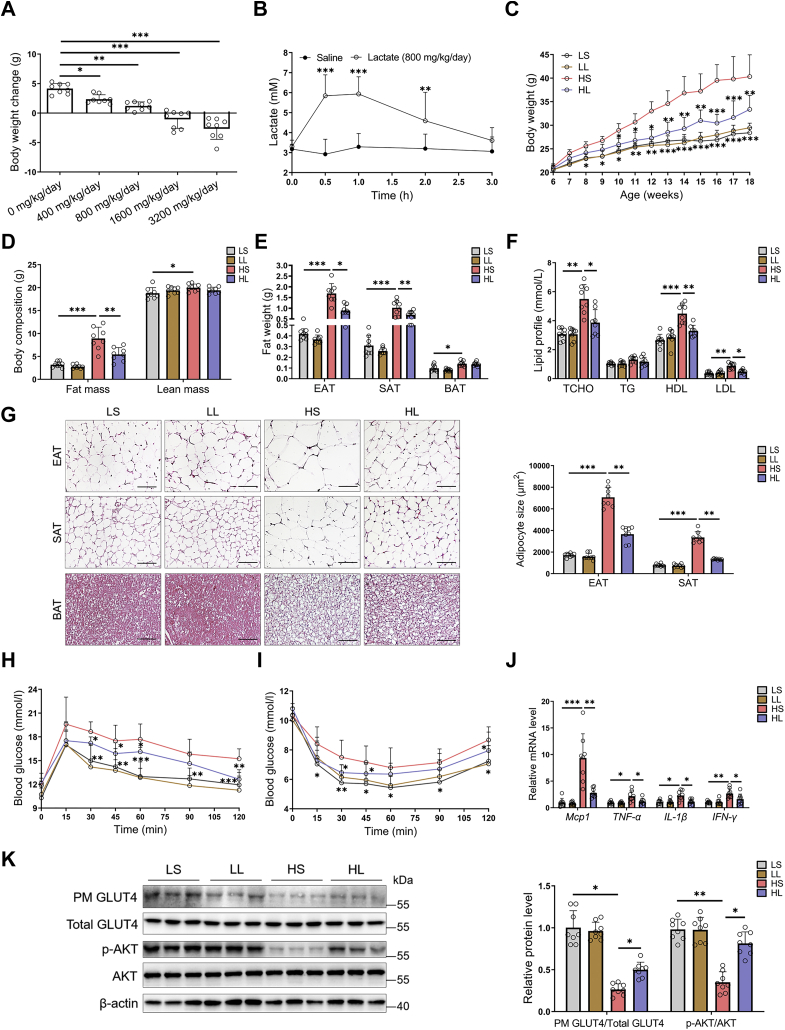
Figure 1.
Moderatel-lactate administration ameliorated obesity and associated insulin resistance in mice. At 6 weeks old, HFD-fed male mice were given with a gradient l-lactate injection. A, body weight changes after gradient l-lactate injection. B, the fluctuations of plasma l-lactate concentration after 800 mg/kg/day injection. In another independent study, 6-week-old male mice were divided into four groups, including LS, LL, HS, and HL groups, and were fed with LFD or HFD for 12 weeks, respectively. C, the body weights. D, the body composition. E, the fat weights. F, serum lipid profile. G, the adipose tissue H&E staining and adipocyte size; the scale bar represents 100 μm. H and I, the GTT (H) and ITT (I). J, the mRNA levels of proinflammatory cytokines in EATs. K, insulin signaling cascades in EATs in mice without insulin injection. The GLUT4 translocation in EATs and quantification of plasma membrane GLUT4 to total GLUT4; immunoblots for phospho-AKT (Ser-473) and total AKT in EATs and quantification of phosphorylated AKT to total AKT. Data are presented as mean ± SD of eight mice per group, one-way ANOVA with Mann–Whitney test; ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001. EAT, epididymal adipose tissue; GLUT4, glucose transporter type 4; GTT, glucose tolerance test; HFD, high-fat diet; HS, HFD-saline (i.p.); HL, HFD-lactate (i.p.); ITT, insulin tolerance test; LFD, low-fat diet; LL, LFD-lactate (i.p.); LS, LFD-saline (i.p.); PM, plasma membrane.