Figure 2.
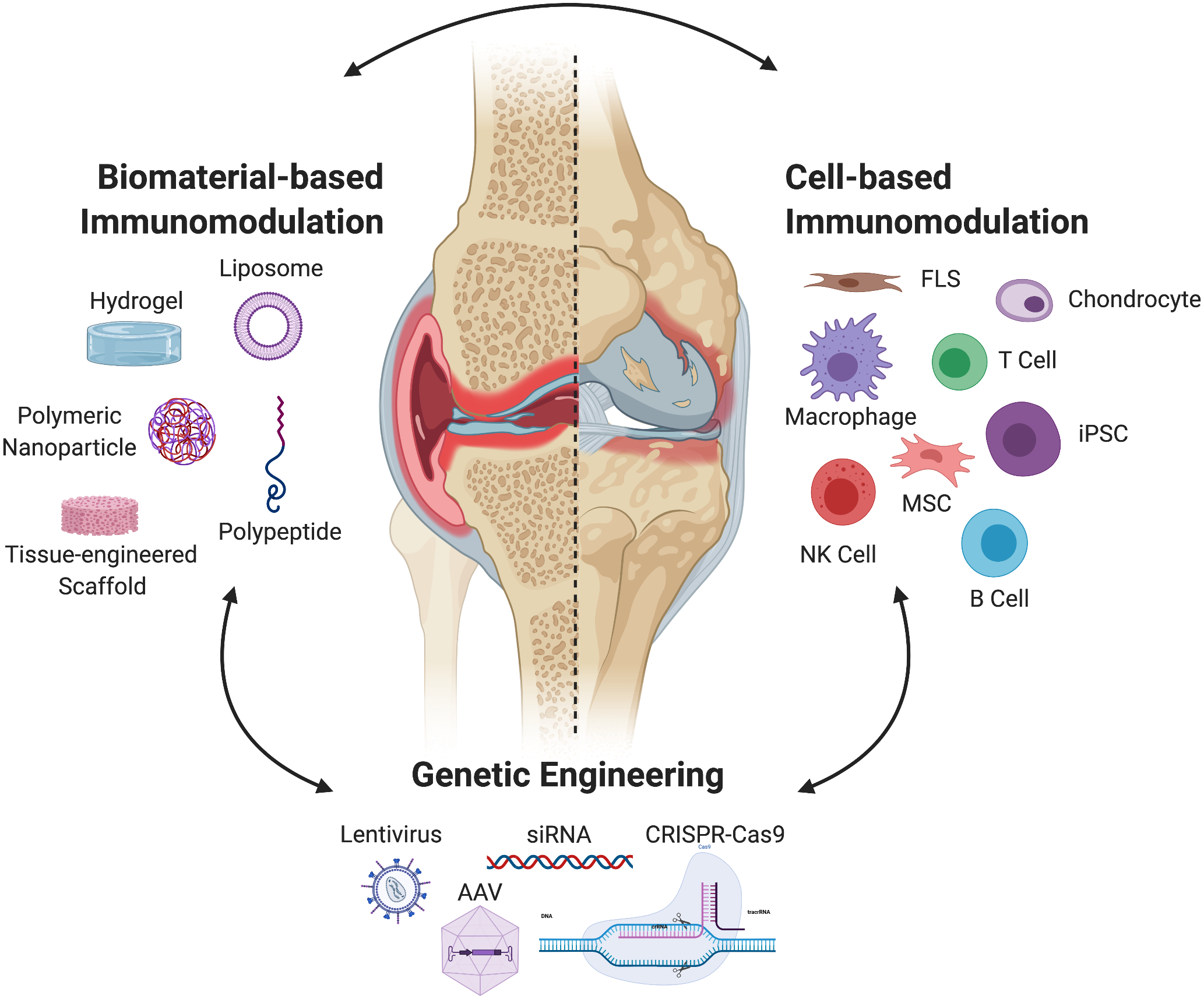
Current immunomodulatory strategies rely on three types of approaches: (1) the exogenous delivery of autologous or allogenic cells, (2) genetic engineering or gene therapy to alter resident and exogenous cell populations, or (3) biomaterial-based systems that act by themselves as immunomodulators as well as aid in the delivery of cells or material for genetic engineering of resident cell populations. While each of these strategies may be used on their own, many immunoengineering approaches combine their use for the design of more controlled and precise treatment. Abbreviations: FLS: Fibroblast-like synoviocytes; MSC: Mesenchymal stem cells; iPSC: Induced pluripotent stem cell; NK: Natural killer cell; CRISPR-Cas9: Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats, (CRISPR)-associated protein 9; siRNA; small interfering RNA; AAV: adeno-associated virus.
