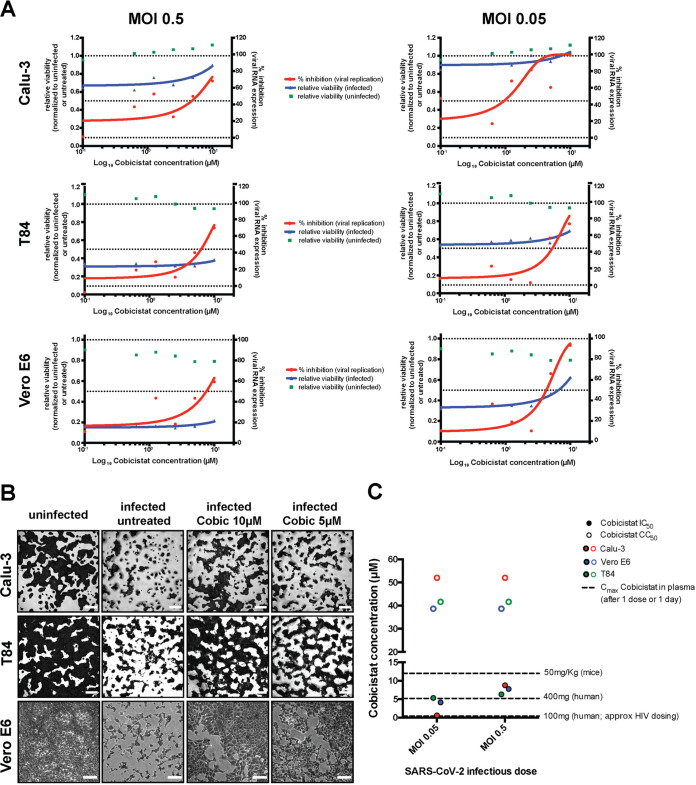
FIG 2.
Cobicistat decreases replication of SARS-CoV-2 and rescues viability of infected cells in multiple in vitro models. (A and B) Effect of serial dilutions of cobicistat on SARS-CoV-2 RNA concentration in supernatants (A) and on the viability of infected and uninfected cell lines of lung (Calu-3), gut (T84), and kidney (Vero E6) origin (A and B). Cells were infected with SARS-CoV-2 at two different MOIs (0.05 and 0.5) and left untreated or treated with cobicistat 2 h postinfection. Forty-eight hours postinfection, supernatants were collected and viral RNA was assayed by qPCR while cellular viability was measured by MTT assay (A) or by crystal violet staining (B). Inhibition of viral replication was calculated as described in Materials and Methods while viability data were normalized to the uninfected or to the untreated control. Half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values were calculated by nonlinear regression. Each point in panel A represents a mean from 3 independent experiments. Pictures in panel B are derived from infections at MOI 0.5 (Calu-3 and T84 cells) or MOI 0.05 (Vero E6 cells). (C) Comparison between the IC50 and CC50 values of cobicistat determined in vitro and the peak plasma levels detectable in mice (Pharmacology Review of Cobicistat - application number: 203-094) and in humans (33, 81) after administration of a single dose of the drug. Determination of in vitro CC50 values is based on the data shown in Fig. S2.