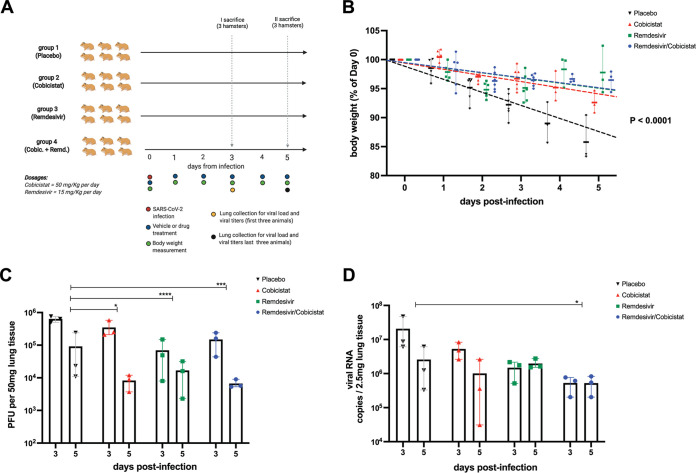
FIG 6.
The combination of cobicistat and remdesivir inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication and disease progression in Syrian hamsters. (A) Schematic representation (created with BioRender) of the in vivo dosing and sample collection of Syrian hamsters infected with SARS-CoV-2 and treated with placebo, cobicistat, remdesivir, or a combination of cobicistat and remdesivir. (B) Weight loss progression over time in the placebo and each treatment group. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD of the percentage over the baseline (day 0 postinfection [p.i.]) weight of each animal (n = 6 until day 3 p.i. and n = 3 at days 4 to 5 p.i.). Data were analyzed by linear regression for each experimental group, followed by the parametric F-test to assess differences among slopes. (C and D) Replication-competent viral titers as PFU on Vero E6 cells (C) and gRNA viral levels in the lung as measured at day 3 (n = 3) and 5 (n = 3) p.i. by plaque assay (C) and qPCR (D) quantification. Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s posttest, comparing the cumulative effects of treatments at both day 3 and day 5 p.i. Before the statistical analysis, an appropriate transformation was applied to make the results uniform (i.e., exponential transformation for PFU and standard log transposition for viral RNA copy numbers, due to the respective size-dependent restriction or amplification of the signal derived from the tests adopted). *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001.