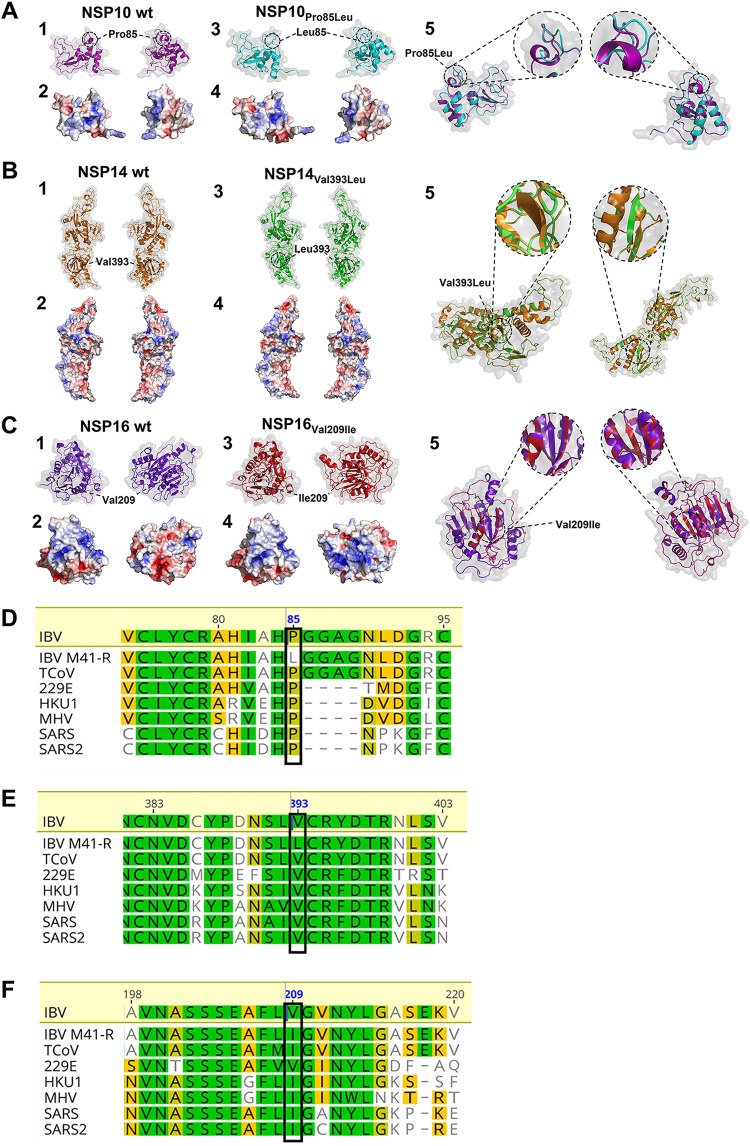
FIG 9.
The amino acids at residue 85 in nsp 10 and 393 in nsp 14 are conserved among members of the coronavirus family with the change Pro85Leu in Nsp 10 predicted to affect the secondary protein structure. (A through C) Structural models of WT M41-CK nsp 10 and nsp 10 containing Pro85Leu, (E) WT M41-CK nsp 14 and nsp 14 containing Val393Leu, and (F) WT M41-CK nsp 16 and nsp 16 containing Val209Ile. All models were generated using SWISS-MODEL and visualized using PyMol using crystal structures of SARS-CoV nsps 10, 14, and 16 as the templates, RCSB PDB, 2XYV; RCSB PDB, 5C8T; and RCSB PDB, 2XYV; respectively. Each panel highlights specific viewpoints, with panels D2, D4, E2, E4, F2, and F4 highlighting the electrostatic mapping. Modeling of nsp 10 indicated that the presence of a leucine instead of a proline at residue 85 caused the loss of an α-helix and replaced it with an extended loop. The location and structural difference are highlighted in panel A5. (D to F) Amino acid alignment comparing the amino acid sequence in rIBV M41-R to HCoV-229E (GenBank accession no. KF514433), HCoV-HKU1 (NC_006577), IBV M41-CK (MK728875), MHV (KF268339), SARS-CoV (KF514395), SARS-CoV-2 (NC_045512), and turkey coronavirus (TCoV) (NC_010800). (D) Boxes indicate residue 85 in nsp 10, (E) residue 393 in nsp 14, and (F) residue 209 in nsp 16. MAFTT alignment has been generated using Geneious version 10.2.3 with colors displaying the percentage of similarity following Blosum80 score matrix.