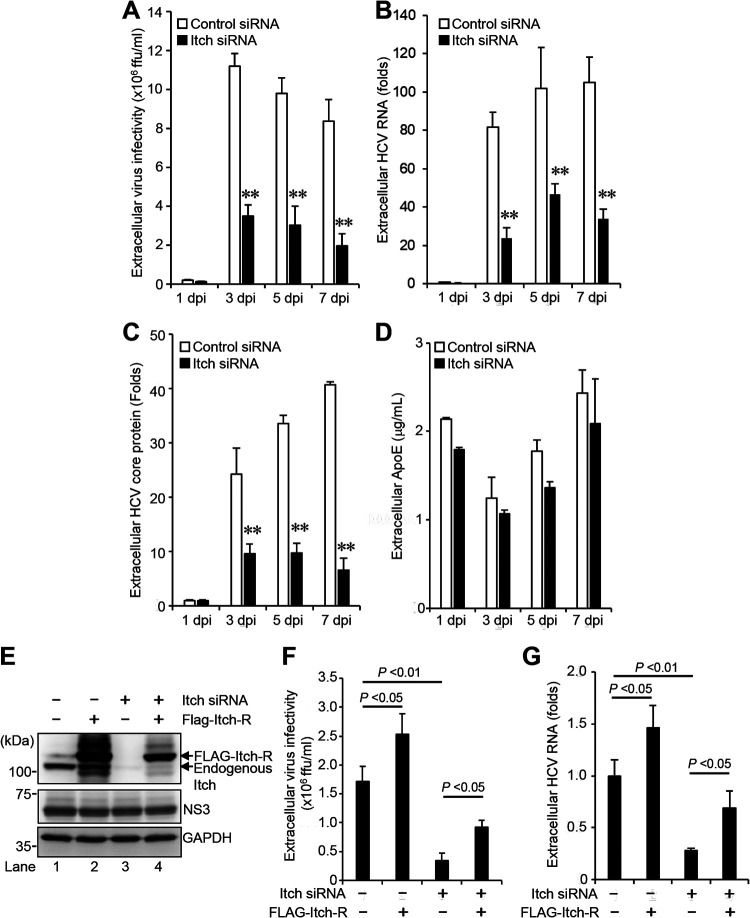
FIG 3.
Knockdown of Itch decreases the release of HCV particles. (A) Huh-7.5 cells were transfected with 40 nM Itch siRNA or control siRNA. At 24 h posttransfection, cells were infected with HCV J6/JFH1 at an MOI of 2. The culture supernatants were collected at 1, 3, 5, and 7 dpi. The extracellular virus infectivity was measured by a focus-forming assay. (B) Extracellular HCV RNA was extracted and quantitated by RT-qPCR. The value for the control siRNA-transfected cells at 1 dpi was arbitrarily expressed as 1.0. (C) The amount of extracellular HCV core protein was measured by core ELISA. The value for the control siRNA-transfected cells at 1 dpi was arbitrarily expressed as 1.0. Data represent means ± SEM of data from three independent experiments; **, P < 0.01 compared with the controls. (D) The amount of extracellular ApoE protein was measured by the human ApoE ELISA kit. (E) Huh-7.5 cells were transfected with 40 nM Itch siRNA or control siRNA. At 24 h posttransfection, cells were infected with HCV J6/JFH1 at an MOI of 2. At 3 h postinfection, cells were transfected with Itch siRNA-resistant plasmid pCAG-FLAG-Itch-R. At 72 h after plasmid transfection, the cells were harvested, and cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-Itch MAb, anti-NS3 MAb, and anti-GAPDH MAb. The level of GAPDH served as a loading control. (F) Culture supernatants were collected, and the extracellular virus infectivity was measured by a focus-forming assay. (G) The extracellular HCV RNA was extracted and quantitated by RT-qPCR (G). Data represent means ± SEM of data from three independent experiments.