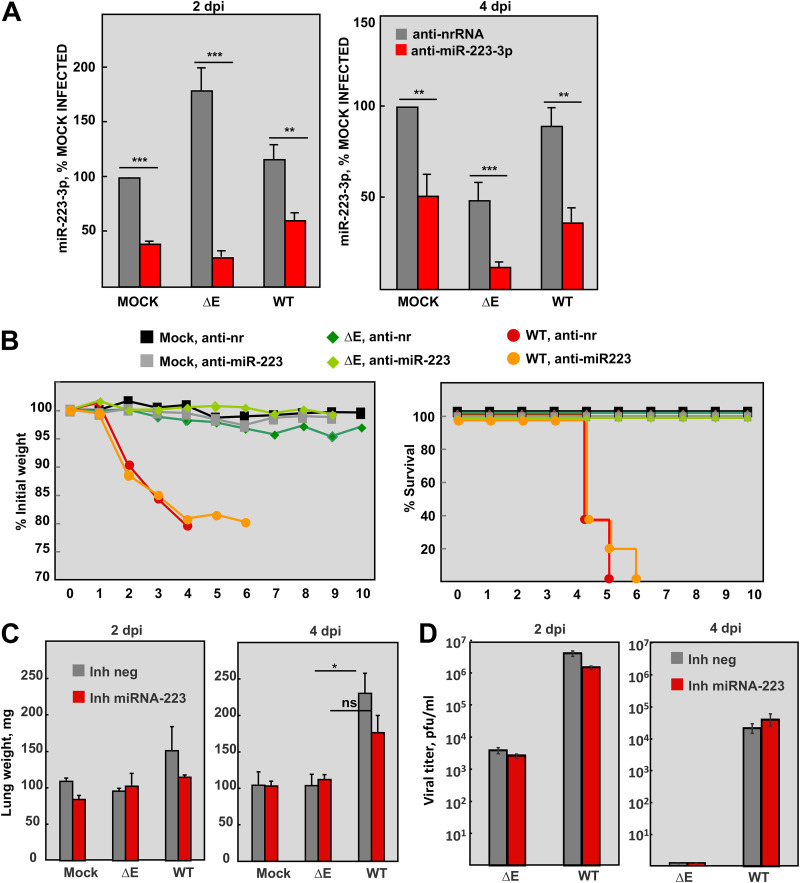
FIG 3.
Analysis of miRNA-223-3p in SARS-CoV-infected mice using antisense LNA inhibitors. BALB/c mice were intranasally inoculated with 200 μg (10 mg/kg) of the LNA miRNA-223-3p inhibitor or a nonrelated sequence (nrRNA) as a negative control. After 24 h, the mice were infected with 105 PFU of SARS-CoV-ΔE or -WT and their lungs were collected at 2 and 4 days p.i. n = 11 mice were mock-infected or infected with each virus and treated with miRNA-223-3p inhibitor or a negative control. At 2 and 4 days p.i., n = 3 mice per experimental condition were sacrificed for analysis of lung RNA, viral titer, and histopathology. (A) RT-qPCR analysis of miRNA-223-3p levels in the lungs, relative to the expression in mock-infected mice inoculated with the nrRNA. The ΔΔCt method was used for relative quantification, with snRNA-U6 as the endogenous control. (B) The weight loss (left graph) and survival (right graph) of mice was monitored during 10 days. Weight loss was expressed as the percentage of the initial weight measured before infection. (C) Weight of the lungs of mice at 2 and 4 days p.i. Lungs were weighted when collected and prior to fixation. (D) Viral titers in the lungs of infected mice. At 2 and 4 days p.i., 3 mice from each group were sacrificed to determine virus titers. Error bars indicate the standard error of the mean from 3 mice lungs per each condition. Statistical significance was calculated by two-tailed Student´s t test. ns, nonsignificant; *, P value < 0.05.