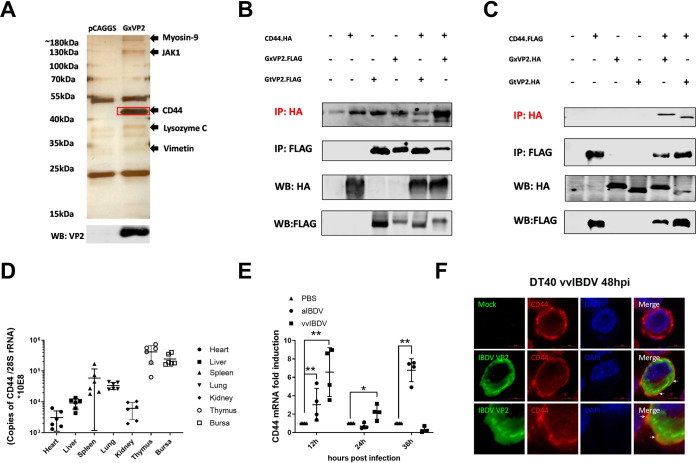
FIG 1.
Screening and identification for host protein of bursal lymphocytes interacting with IBDV VP2. (A) Possible VP2-interacting proteins were identified and listed by LC-MS analysis, including chicken CD44 (chCD44) at ∼43 kDa. (B-C) Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) results indicated the interaction between chCD44 extracellular domain and capsid protein VP2. Western blot analysis using anti-HA-tag antibody shows the bands corresponding to the chCD44 extracellular domain (B). Western blot analysis using the antibody against the HA-tag shows the bands corresponding to the vvIBDV (Gx strain) and aIBDV (Gt strain) VP2 (C). (D) ChCD44 transcription levels in organs (Heart, liver, spleen, lung, kidney, thymus, and the bursa of Fabricius) of 3-week-old SPF chickens. (E) Transcription level of chCD44 in SPF chicken bursa at different time points after vvIBDV or aIBDV infection. ChCD44 mRNA levels were significantly induced by vvIBDV at 12 and 24 hpi and aIBDV at 12 and 36 hpi (P < 0.05), compared with the mock-infected group. Data represent means ± standard deviations (n = 3). (F) Colocalization between VP2 and chCD44 in vvIBDV infected DT40 cells. DT40 cells were infected by vvIBDV (mock infection group as negative control) and conducted the confocal analysis. The results indicated that chCD44 (red fluorescence) was co-localized with IBDV VP2 (green fluorescence, lower panel), while VP2 (green fluorescence) was not detected in the mock-infected groups (upper panel). White arrows were pointing to the co-localtion between chCD44 and VP2.