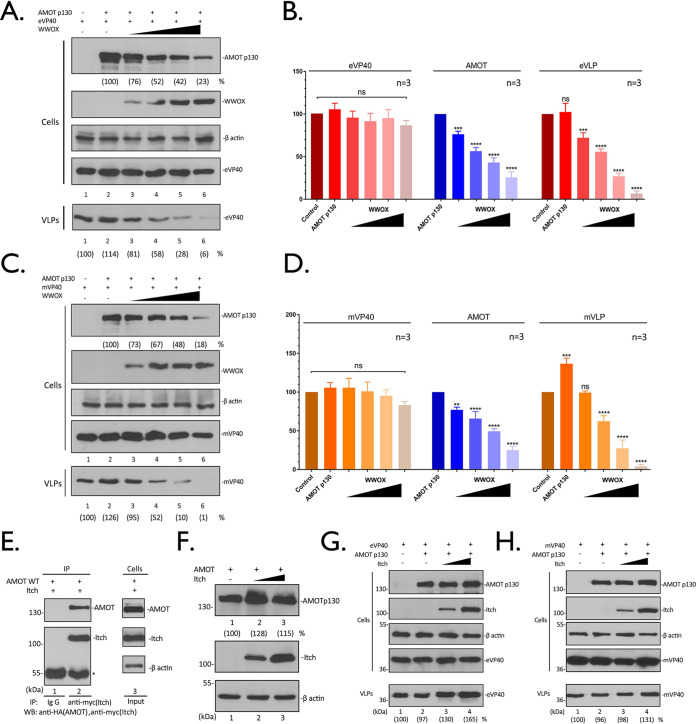
FIG 5.
WWOX suppresses AMOT expression and inhibits VP40 VLP egress. (A and C) HEK293T cells were transfected with a constant amount of eVP40 (A), mVP40 (C), and AMOT plus vector alone (−) or increasing amounts of WWOX. The indicated proteins were detected in cell extracts and VLPs by WB. The cellular levels of AMOT, eVP40, mVP40, and VP40 in VLPs were quantified using NIH ImageJ. The amounts of eVP40 (A, cells, lane 1), mVP40 (C, cells, lane 1), and AMOT (A and C, cells, lane 2) in control cells were set at 100%. Also, eVP40 (A, VLPs, lane 1) and mVP40 (C, VLPs, lane 1) VLP production from control cells was set at 100%. Numbers in parentheses represent relative protein levels and VLP budding efficiency compared to the control. (B and D) Quantification of the indicated cellular protein levels and relative budding efficiency of eVP40 (B) and mVP40 (D) VLPs from three independent experiments. Statistical significance was analyzed by a one-way ANOVA. ns, not significant; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001. (E) Extracts from HEK293T cells transfected with myc-tagged Itch and HA-tagged AMOTp130 were IP with either normal mouse IgG or anti-myc antibody. AMOTp130 and Itch were detected in the precipitates by WB. (F) HEK293T cells were transfected with AMOTp130 plus vector alone (−) or increasing amounts of Itch. The indicated proteins were detected by WB, and AMOTp130 expression levels were quantified. (G and H) HEK293T cells were transfected with a constant amount of eVP40 (G), mVP40 (H), and AMOTp130 plus vector alone (−) or increasing amounts of Itch. The indicated proteins were detected in cell extracts and VLPs by WB, and VP40 in VLPs was quantified using NIH ImageJ (numbers in parentheses).