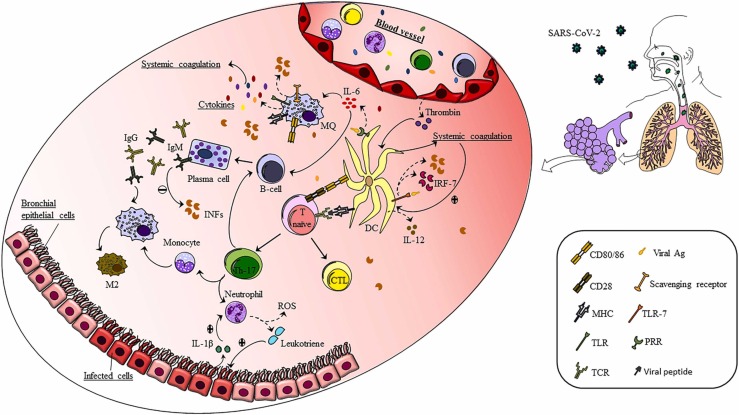
Fig. 1.
The role of APCs in the progression of COVID-19 disease. After the infection with SARS-CoV-2 binds to the target cell, the innate immune system and innate immune cells such as dendritic cells, macrophages, and granulocytes are activated. These cells, in turn, secrete a complex of pro-inflammatory cytokines that activate the humoral and cellular immune systems. The activation of B cells, and the hypersecretion of antibodies, causes an over-response of the immune system, resulting in tissue damage. T cells also lead to excessive penetration of neutrophils and monocytes into the area of infection, resulting in lung tissue damage and clinical symptoms exacerbation.