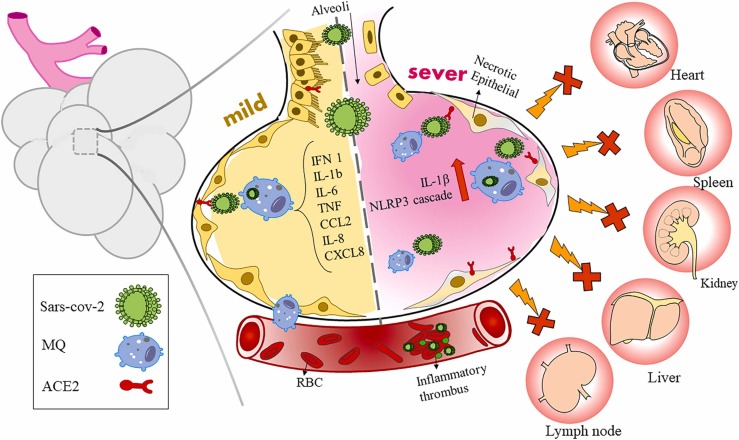
Fig. 2.
The role of pulmonary macrophages in mild and severe cases. After the migration of monocyte-derived macrophages from the capillaries into the lung alveoli, macrophages are produced by the uptake of virus-infected cytokine-infected epithelial cell debris and inflammatory-induced chemokines. Gradually, with the intensification of inflammation, over-activation of macrophages due to the production of inflammatory lipids from damaged cells, the accumulation of immune cells at the site of infection and disruption of the ratio of monocytes to macrophages, the expression of ACE2 receptors on the surface of these cells increased, so the viruses spread to other organs and disrupts them.