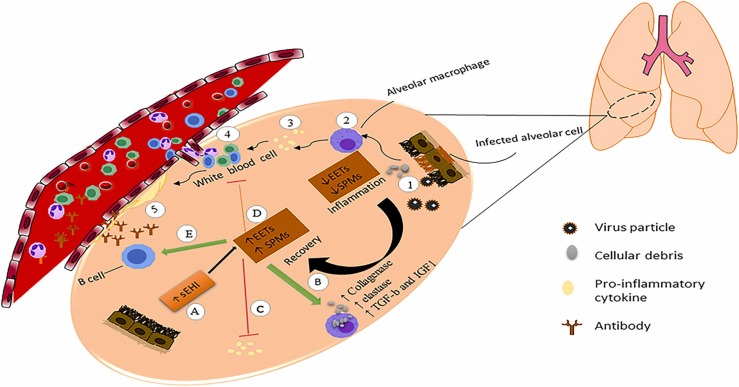
Fig. 3.
Role of macrophage in recovery COVID-19 infection Inflammation: Alveolar cells infected by viral particle and apoptotic and necrotic debris accumulated (1) macrophages uptake debris (2) debris motivate the generation of pro-inflammatory cytokines of macrophages (3) pro-inflammatory cytokines increase infiltration of immune cell (4) infiltration of the immune cell increased hyaline membrane formation and cause acute respiratory distress syndrome (5). Recovery: EETs and SPMs are reduced in a severe inflammatory condition. During recovery, EETs increase, then EETs increase the production of SPMs (A). SPMs stimulate macrophage phagocytosis (B), reduce pro-inflammatory cytokine(C), inhibit leukocytosis, and thereby decrease the infiltration of leukocytes (D) and may facilitate the adaptive immune response and enhance the production of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies (E).