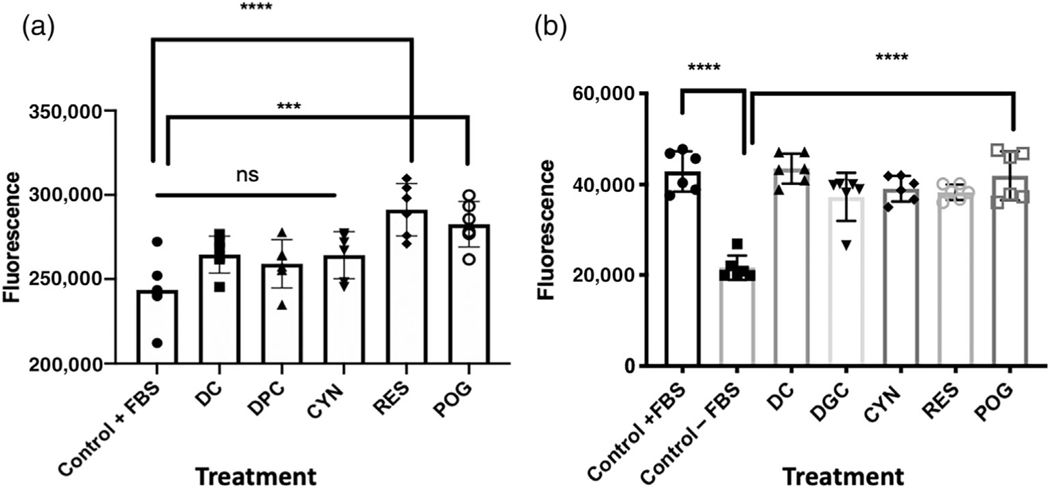
FIGURE 1.
Treatment of cultured human hFOB osteoblasts with resveratrol and anthocyanins. (a) hFOB cells were grown in media containing 10% FBS and then treated with anthocyanins for 72 hr. Control cells were treated with 0.01% DMSO. Cells were treated with delphinidin (DC); delphinidin-O-glucoside (DGC); cyanidin (CYN); resveratrol (RES); peonidin-3-O-glucoside (POG) in a concentration of 1.0 μg/ml. Control vs. DC, DGC, CYN was not significant (ns), while treatments with RES or POG significantly increased cell proliferation (***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001). (b) hFOB osteoblasts were serum-starved for 24 hr and then treated with anthocyanins for 72 hr. As compared with osteoblasts grown in media with 10% FBS, serum-starved (−FBS) cells showed a significant (p < 0.0001) reduction in growth. However, treatment of serum-starved cells with DC, DGC, CYN, RES, or POG increased cell proliferation and reduced apoptosis at a concentration of 1.0 μg/ml. Control + FBS vs. Control – FBS (****p < 0.0001); Control −FBS vs. DC, DGC, CYN, RES, POG (****p < 0.0001). Cell viability and proliferation were measured using CellTitreGLo® (Promega). Statistics were performed using one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test using GraphPad 8.2 (San Diego, CA)