Fig. 2.
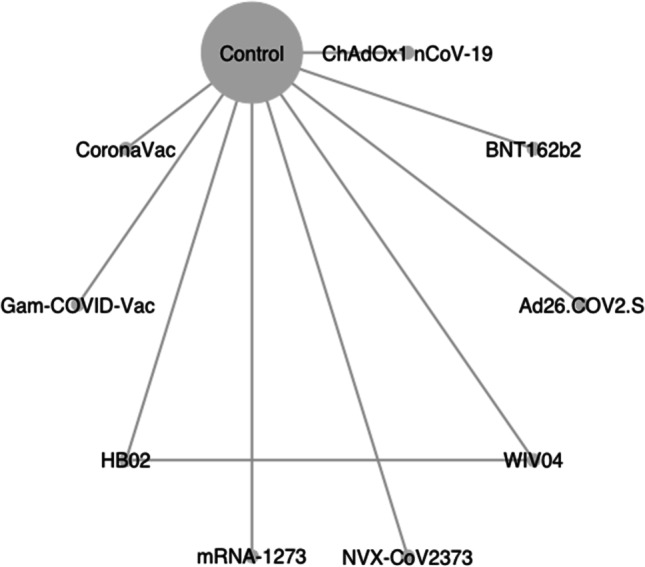
Network graph of eligible COVID-19 vaccines comparisons for efficacy. Line width is proportional to the number of trials comparing every pair of vaccine. The size of the circle is proportional to the number of participants assigned to receive the vaccine; BNT162b2 (lipid nanoparticle-formulated, nucleoside-modified RNA encoding the SARS-CoV-2 full-length spike): 30 μg; ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (AZS1222): recombinant-deficient chimpanzee adenoviral vector containing the SARS-CoV-2 structural glycoprotein antigen (spike protein; nCoV-19): 2.2–6.5×1010 viral particle (VP); mRNA-1273 lipid nanoparticle (LNP)-encapsulated modified RNA encoding the perfusion stabilized full-length spike protein of the SARS-CoV-2 virus): 100 μg; WIV04 (5 μg) and HB02 (4 μg): inactivated SARS-CoV-2 strains created from Vero cells with aluminum hydroxide adjuvant; Gam-COVID-Vac: heterologous prime-boost which combined two vector vaccine based on rAd type 26 (rAd26) and rAd type 5 (rAd5) carrying the gene for SARS-CoV-2 full-length glycoprotein S; Ad26.COV2.S: replication-incompetent adenovirus type 26 (Ad26) vectored vaccine encoding a stabilized variant of the SARS-CoV-2 S protein (5×1010 VP); NVX-CoV2373: recombinant nanoparticle encoding the full-length spike glycoprotein of the prototype strain plus Matrix-M adjuvant (5 μg of NVX-CoV2373 plus 50 μg of Matrix-M adjuvant); CoronaVac: inactivated whole-virion SARS-CoV-2 vaccine (3 μg of SARS-CoV-2 virion plus 0.45 mg/ml of aluminum hydroxide)
