Fig 5. Blocking translational initiation generally does not diminish activation of mitochondrial surveillance pathways.
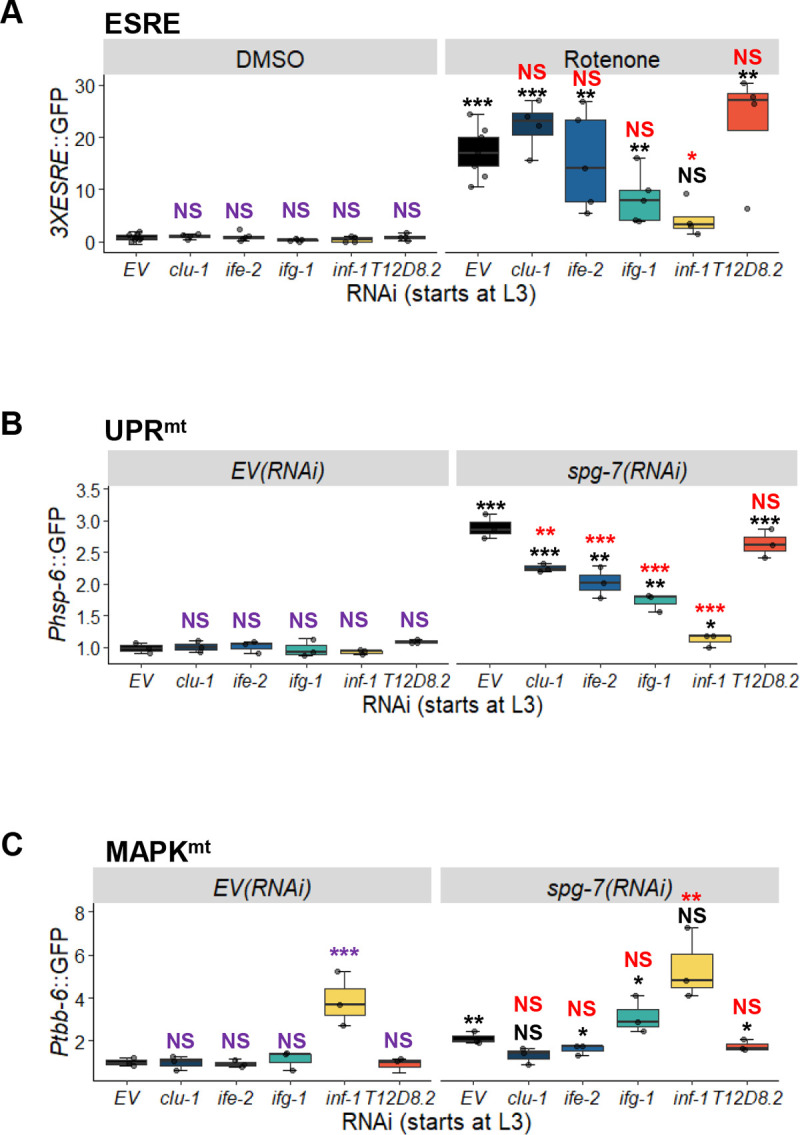
Quantification of GFP fluorescence of C. elegans carrying 3XESRE::GFP (A), Phsp-6::GFP (B), or Ptbb-6::GFP (C) reporters that were reared on E. coli expressing empty vector (EV) or RNAi targeting the eukaryotic initiation factors clu-1/eIF3A, ife-2/eIF4E, ifg-1/eIF4G, inf-1/eIF4A, or T12D8.2/eIF4H. (A) Worms were treated for 8 hours with vehicle (DMSO) or 50 μM rotenone. (B, C) Worms were stressed with spg-7(RNAi), and an empty vector (EV) control was included. Three biological replicates with ~400 worms/replicate were analyzed. p-values were determined from two-way ANOVA, followed by Dunnett’s test, or Student’s t-test. All fold changes were normalized to DMSO-EV or EV control. NS not significant, *p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001. In all panels, purple significance marks indicate comparison between gene(RNAi) and EV(RNAi) in unstressed condition (DMSO or EV(RNAi)), red marks indicate comparison between gene(RNAi) and EV(RNAi) in stressed condition (rotenone or spg-7(RNAi)), and black marks indicate comparison between stressed and unstressed conditions.
