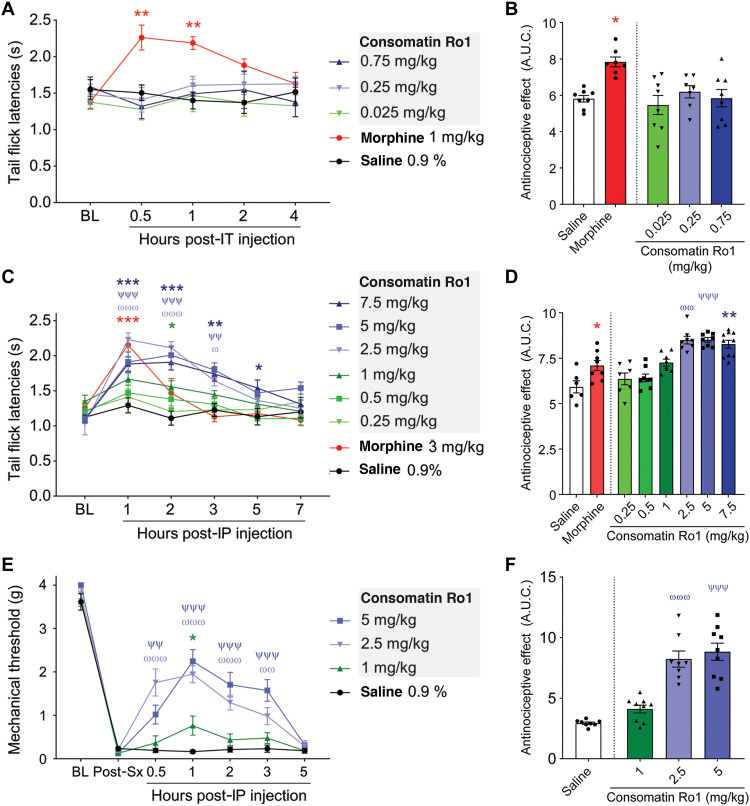
Fig. 6. Consomatin Ro1 provides analgesia in two mouse models of acute pain.
(A and B) Sensitivity to thermal noxious stimuli was evaluated by dipping mouse tails into hot water (52°C) and recording tail flick latencies (TFLs). (A) Mouse TFLs after a single intrathecal injection of saline, morphine, or multiple doses of Consomatin Ro1. TFLs were captured over a 4-hour period [n = 7 to 8 per group, two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Dunnett’s post hoc test]. (B) Area under the curve between baseline (BL) and 4-hour condition, presenting global TFLs when animals received intrathecal (IT) injections (Kruskal-Wallis followed by Dunn’s post hoc test). (C) Mouse TFLs after a single intraperitoneal (IP) injection of saline, morphine, or multiple doses of Consomatin Ro1. TFLs were captured over a 7-hour period (n = 6 to 10 per group, two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test). (D) Area under the curve (A.U.C.) between baseline and 7-hour condition, presenting global TFLs when animals received intraperitoneal injections (Kruskal-Wallis followed by Dunn’s post hoc test). (E) Analgesic effect of Consomatin Ro1 on acute postsurgical pain. Plantar incision surgery intraperitoneal injections. Mechanical sensitivity was assessed using von Frey filaments (n = 8 to 9 per group, two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test). (F) Area under the curve between baseline and 5-hour condition, presenting mechanical withdrawal thresholds when animals received intraperitoneal injections (Kruskal-Wallis followed by Dunn’s post hoc test). Results correspond to means ± SEM. */ω/ψP < 0.05, **/ωω/ψψP < 0.01, and ***/ωωω/ψψψP < 0.001. Red asterisks illustrate significant difference between morphine and saline condition, blue asterisks: 7.5 mg versus saline, ψ: 5 mg versus saline, ω: 2.5 mg versus saline, green asterisks: 1 mg/kg versus saline.