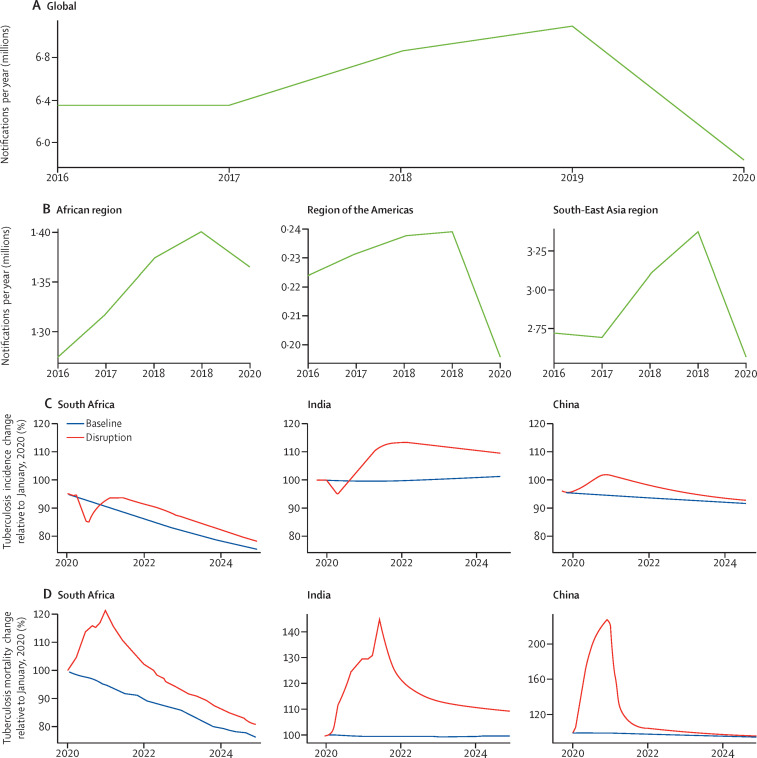
Figure 1.
Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on global, regional, and national tuberculosis detection and mortality
There has been a substantial decline in tuberculosis case detection globally of about 18% in newly ill people reported with tuberculosis at the global (A), regional (B), and national (C) levels, across key regions. Modelling has predicted that this acute drop will probably be followed by a rebound increase in tuberculosis incidence (C); data from three exemplar countries are shown relative to baseline trajectories before COVID-19. The decline in case detection is also estimated to have resulted in an acute increase in mortality in 2020 and is anticipated to take the next few years to reach prepandemic baselines (D); data from three exemplar countries are shown relative to baseline trajectories before COVID-19. Images reproduced by permission of WHO.2