Figure 1.
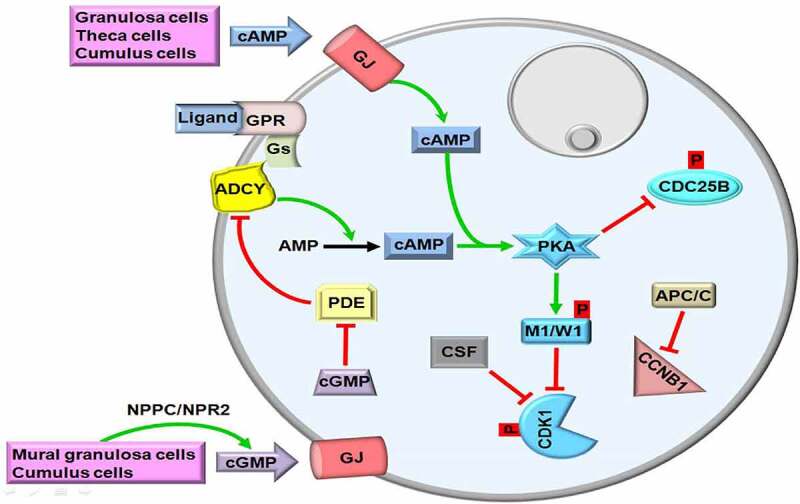
The first meiotic arrest in germinal vesicle (GV) oocytes. Production of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) with adenylyl cyclase (ADCY) by granulosa, theca and cumulus cells activates protein kinase A (PKA) that phosphorylates nuclear kinases, myelin transcription factor 1 (MYT1, abbreviated as M1) and G2 checkpoint kinase (WEE1; abbreviated as W1). Thus, cyclin dependent kinase 1 (CDK1) is remained in a phosphorylated state, and maturation promoting factor (MPF) composed of CDK1 and Cyclin B1 (CCNB1) is repressed. To ensure continuity of meiotic arrest, cAMP in the GV oocytes is holded at high levels via inhibiting phosphodiesterase (PDE) activity with the action of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP). cGMP is generated by mural granulosa and cumulus cells and then transferred though gap junctions (GJs). GPR, G protein-coupled receptor; Gs, G proteins; CSF, Cytostatic factor; CDC25B, Cell division cycle 25B; APC/C, Anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome; NPPC/NPR2, Natriuretic peptide precursor type C/Natriuretic peptide receptor 2; p, Phosphorylation. The GV is depicted by a gray circle at the upper-right site. The green and red arrows represent activation and repression, respectively.
The oocyte in Figure 1 is appearing in an eliptic format. Its original format is in a round format. Please, provide its appearance in a round format as in the word document i have sent a few days ago with e-mail.
