Figure 4.
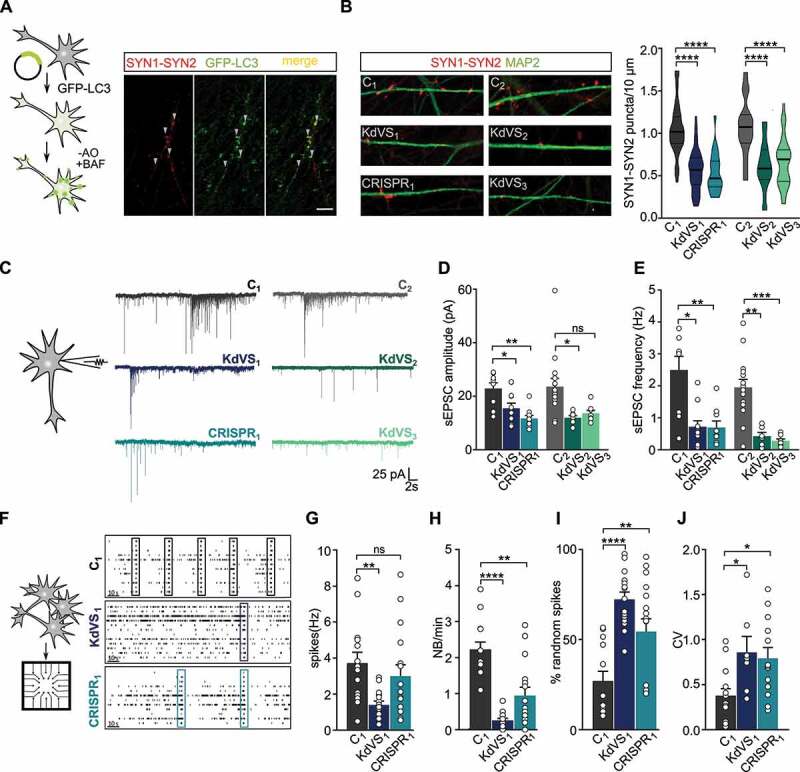
Synaptic phenotype in KdVS patient derived iNeurons. (A) Schematic presentation of the protocol to colocalize LC3 and SYN1-SYN2. Image of a dendrite of a control iNeuron at DIV21 after overnight incubation without B27 and treated with 200 nM BAF for 10 min before fixation. Scale bar: 10 µm. (B) Representative images showing dendrites stained for MAP2 and SYN1-SYN2 and SYN1-SYN2 puncta quantification at DIV21 for all lines. n = 60 for C1; n = 57 for KdVS1; n = 24 for CRISPR1; n = 15 for C2; n = 20 KdVS2; n = 34 for KdVS3. Scale bar: 20 µm. One-way ANOVA and Sidak’s multiple comparison test were used to test for statistically significant differences. (C) Representative voltage clamp recordings at Vh = −60 mV showing sEPSCs at DIV21. (D) sEPSC amplitude and (E) frequency quantification. n = 9 for C1; n = 11 for KdVS1; n = 10 for CRISPR1; n = 15 for C2; n = 8 for KdVS2 and KdVS3 (obtained in two independent experiments). (F) Schematic representation for neuronal network measurements on MEAs (3 min of recording). Representative raster plots for C1, KdVS1 and CRISPR1 derived networks that were plated at similar high densities, measured at DIV 30. (G) Quantification of the mean firing rate and (H) network burst rate, (I) percentage of random spikes, and (J) coefficient of variation (CV) calculated on the inter network burst interval. n = 15 for C1; n = 18 for KdVS1; n = 16 for CRISPR1. If not stated differently, data presented in this figure were obtained in at least 3 independent experiments and statistically significant differences were tested through Kruskal-Wallis and Dunn’s multiple comparison test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.005, ****P < 0.0001.
