Fig. 1. Classical amphiphilic carriers/activators and boron clusters.
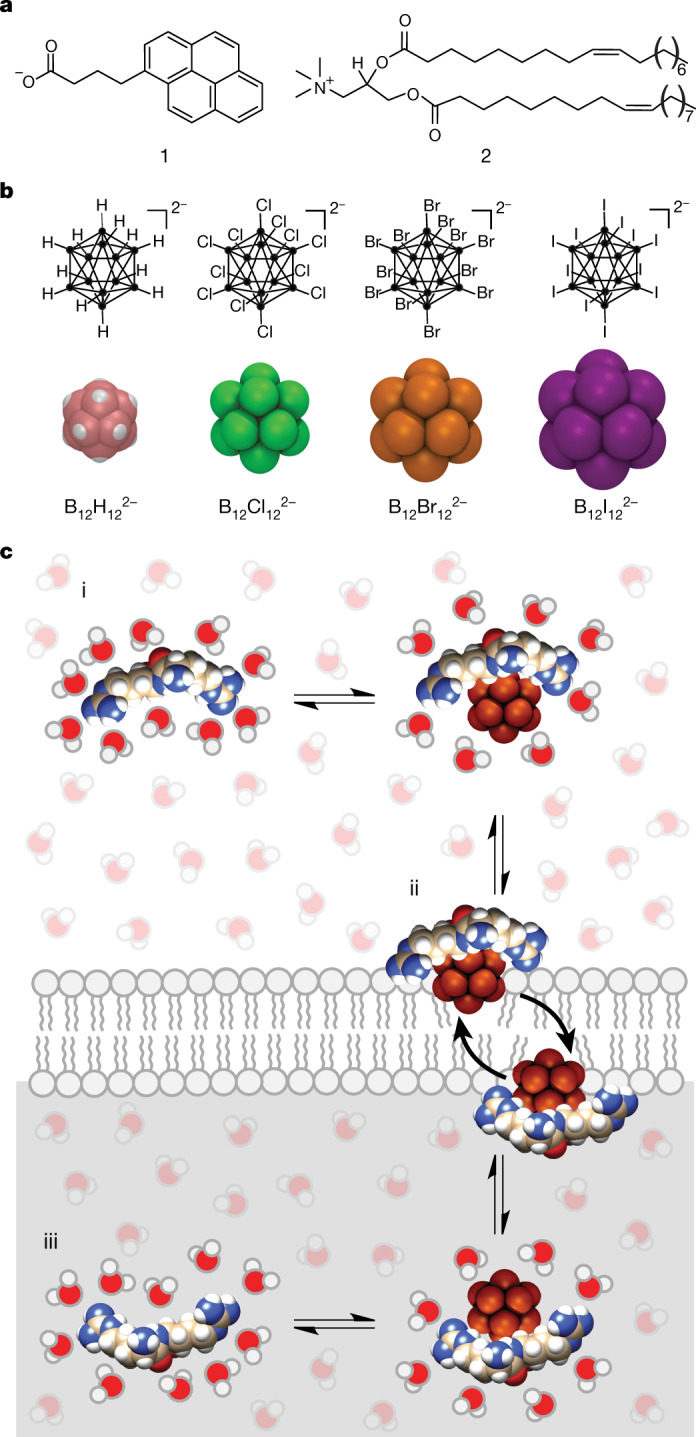
a, Established amphiphilic compounds that act as counterion activator (1) or as carrier (2). b, Chemical structures (top, ● represents boron) and space-filling molecular models (bottom) of dodecaborate (B12X122−) clusters with increasing diameter (8.0–11.8 Å, from refs. 8,9). c, Direct membrane and cargo translocation by superchaotropic clusters. (i) Hydrophilic molecules (for example, an R2 peptide) present a high barrier against desolvation and, thus, cannot interact with/cross the lipid membrane. (ii) The (enthalpy-driven) chaotropic interactions drive desolvation of the cargo and facilitate cargo membrane partitioning and direct translocation. (iii) After membrane passage, the reversible nature of the chaotropic interaction leads to dissociation of the complex and release of the cargo.
