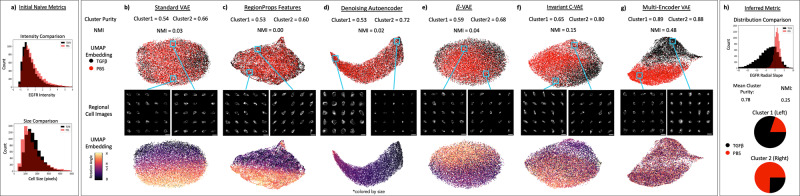
Fig. 2. Separation of biologically distinct cell populations.
a Cells are compared using initial naive metrics such as mean EGFR intensity and cell size to show the difficulty separating the cell populations. b–g The model architectures are quantitatively evaluated using cluster purity and normalized mutual information (k-means with the number of clusters = 2). The sample size for all comparison methods and metrics is n = 15,898 single-cell images. A qualitative comparison is made using visual separation of two labeled cell populations in UMAP embedding space and visual analysis of cells from UMAP regions to identify biologically distinct factors. Rotation angles of cells are shown in UMAP embedding to show the influence of unimportant features on downstream analysis. h The same population of cells is compared using radial slope (a metric inferred from visually analyzing the regional cell images in g). Scale bars in b–g represent 20 μm.