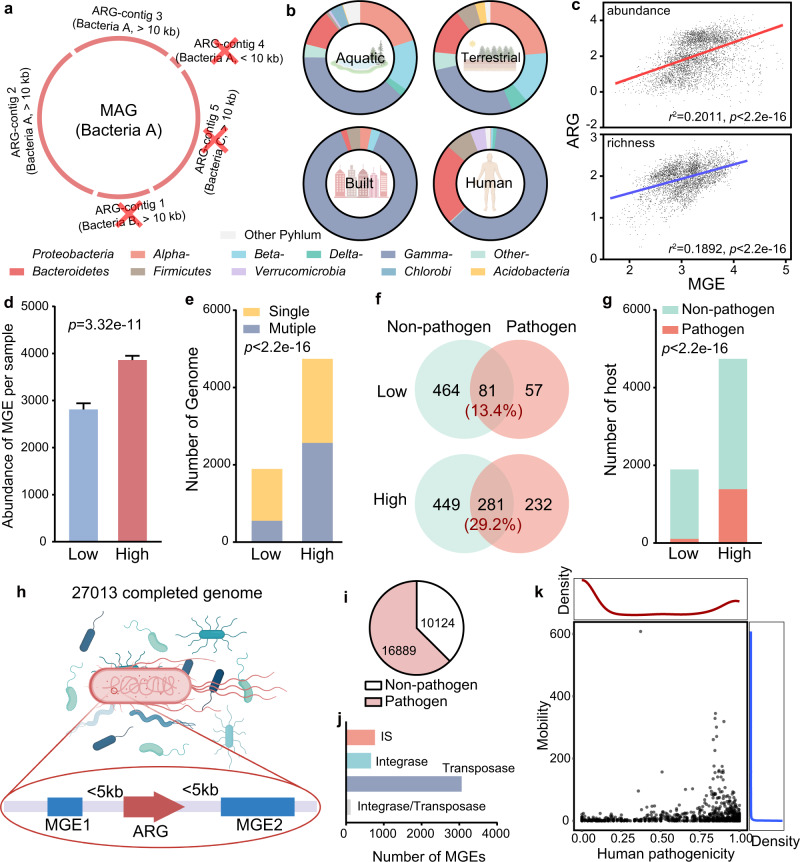
Fig. 2. Human pathogenicity and mobility of ARGs.
a The host of ARGs were determined by only considering ARGs in contigs longer than 10 kb and making sure that the taxonomic affiliation of those ARG-containing contigs agree with the overall taxonomy of the MAG. b Composition of antibiotic resistance host at the phylum level (and classes in Proteobacteria) showed the different distributions of ARG hosts in four main habitats. c MGEs exhibited a significantly positive correlation with ARGs in abundance and richness. Each point represents one sample (n = 4572 samples). The value of abundance and number of ARGs were showed in log10. Result of linear regression are shown as r2 and p value, evaluated by F-statistic (one-sided). d Abundance of MGEs in high-intensity human activities areas were significantly higher than in low-intensity human activities areas. n = 1643 and 2309 biologically independent samples for Low- and High-group, respectively. Significance between two groups was evaluated by two-tailed Welch’s t-test. Data were showed as mean ± standard error of mean (SEM). e Number of genomes containing multiple ARGs increased in high-intensity human activities areas, compared to the low-intensity human activities areas (Fisher’s exact test, one-sided). f Shared ARGs in pathogens or non-pathogen increased in high-intensity human activities areas, compared to low. The percentage of shared ARGs in the two areas are shown. g Pathogenic hosts of ARGs increased in high-intensity human activities areas, compared to low (Fisher’s exact test, one-sided). h We collected 27,013 completed genome from NCBI RefSeq database for determining the human pathogenicity and mobility of ARGs. Five kb upstream and downstream of the ARGs detected in all completed genome for annotating the MGEs. i Among the 27,013 completed genome, 16,889 were recognized as pathogens’ genome. j We totally identified 4612 MGEs from completed genomes, and most of them were referred to the transposase. k The human pathogenicity of ARGs exhibited a bimodal distribution, while most of ARGs (2266/2561) showed mobility <10.