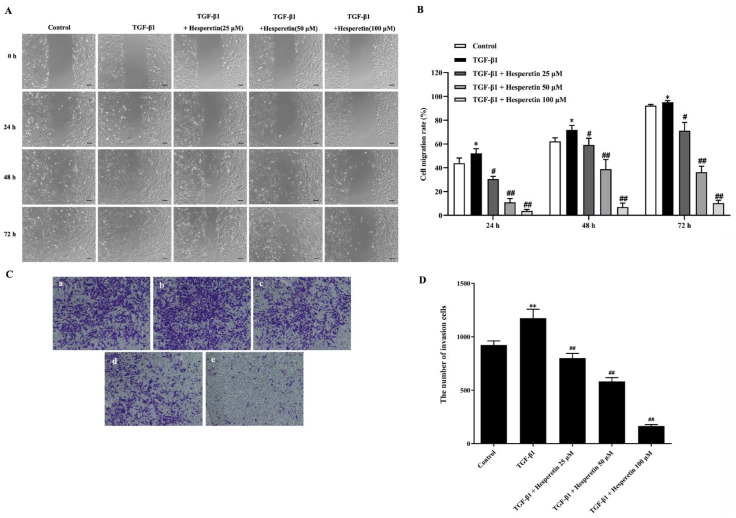
Figure 2.
Hesperetin inhibits the migration and invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells induced by TGF-β1. (A) Wound healing assay was applied to observe the inhibitory effect of hesperetin on the migration of MDA-MB-231 cells induced by TGF-β1. Cells were treated with TGF-β1 positive control or co-incubation of TGF-β1 and (25, 50, and 100 μM) hesperetin. Photos were taken with Keyence fluorescent microscope at 10× magnification at 0, 24, 48, and 72 hour after treatment. Scale bar = 100 μm. (B) The treatment of hesperetin inhibits dose-dependently migration induced by TGF-β1 in MDA-MB-231 cells. Cell migration rate was analyzed using NIH ImageJ software. Each result represents mean ± SD of 6 independent experiments. *P < 0.05 versus control group; #P < 0.05 versus TGF-β1 group; ## P < 0.01 versus TGF-β1 group. (C) Transwell invasion assay was used to evaluate the inhibitory effect of hesperetin on the invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells induced by TGF-β1. a: Control; b: TGF-β1; c: TGF-β1 + hesperetin 25 μM; d: TGF-β1 + hesperetin 50 μM; e: TGF-β1 + hesperetin 100 μM. Photos were taken with Keyence microscope at 10 × magnification at 48 hour after treatment. (D) The statistical figure results show that the TGF-β1-mediated invasion was significantly decreased in a dose-dependent manner in MDA-MB-231 cells after treatment with hesperetin. The number of invading cells was counted using NIH ImageJ software, and statistical analysis of results was analyzed with Graphpad Prism 8.4 software. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD, n = 6. **P < 0.01 versus control group; ##P < 0.01 versus TGF-β1 group.