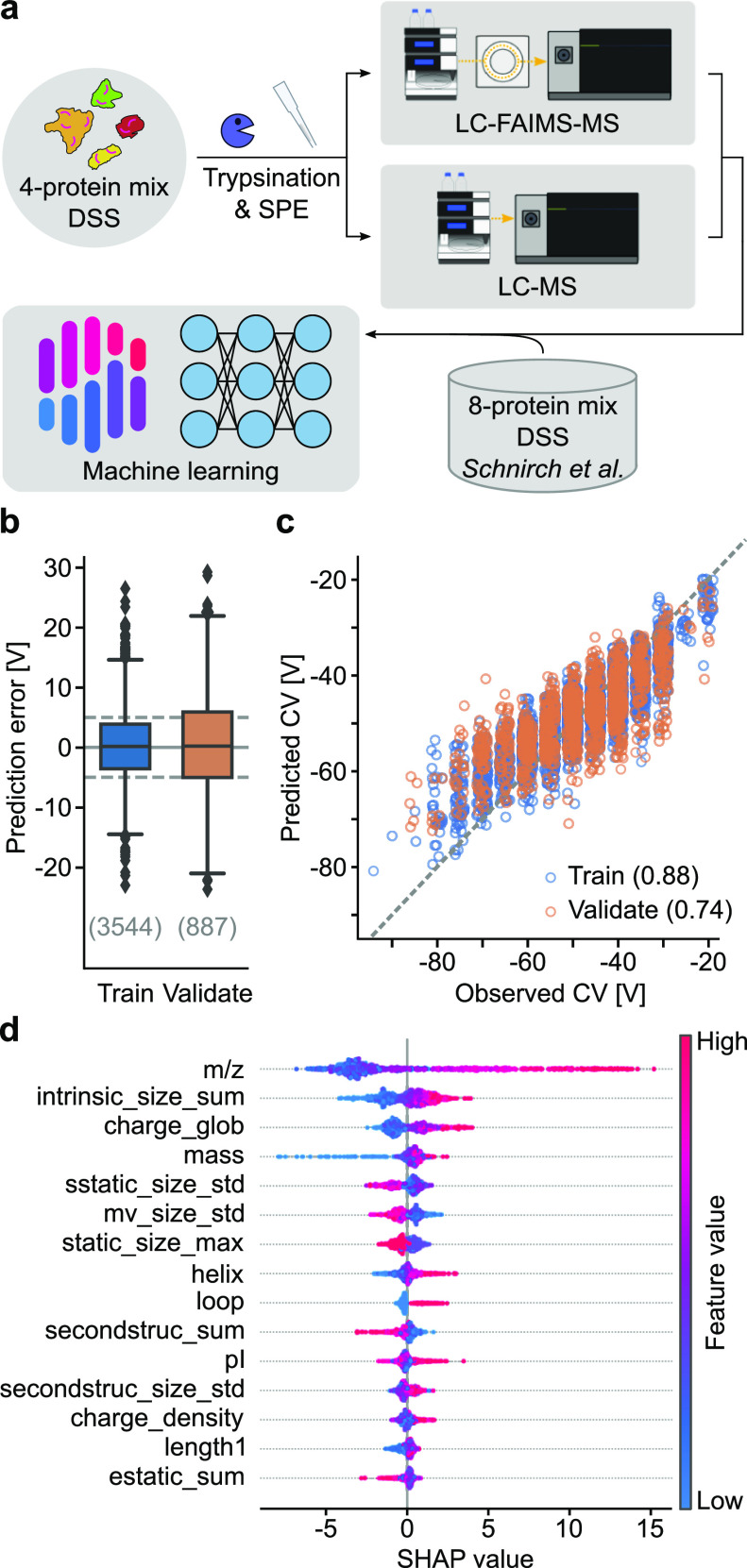
Figure 1.
Machine learning-assisted characterization of cross-linked peptide separation with FAIMS Pro. (a) Experimental workflow. Data from a DSS-cross-linked four-protein mix analyzed by LC-FAIMS-MS or LC–MS were merged with a dataset from Schnirch et al.(10) and subjected to explainable machine learning. (b) Machine learning prediction performance on training and validation data subsets (see Methods for details). Dashed line corresponds to ±5 V error margin. Numbers in brackets indicate the number of data points for each set. (c) Prediction accuracy on training and validation data subset-based CV prediction error. Numbers in brackets represent the Pearson correlation coefficient for each data subset. (d) Global feature importance for differential ion-mobility prediction from the SHAP value analysis. The 15 most important features are shown (declining impact from top to bottom). The feature-specific impact on the prediction is shown on the x-axis. The color gradient illustrates the relative value distribution of a corresponding feature for each CSM (represented by a dot).