Figure 2:
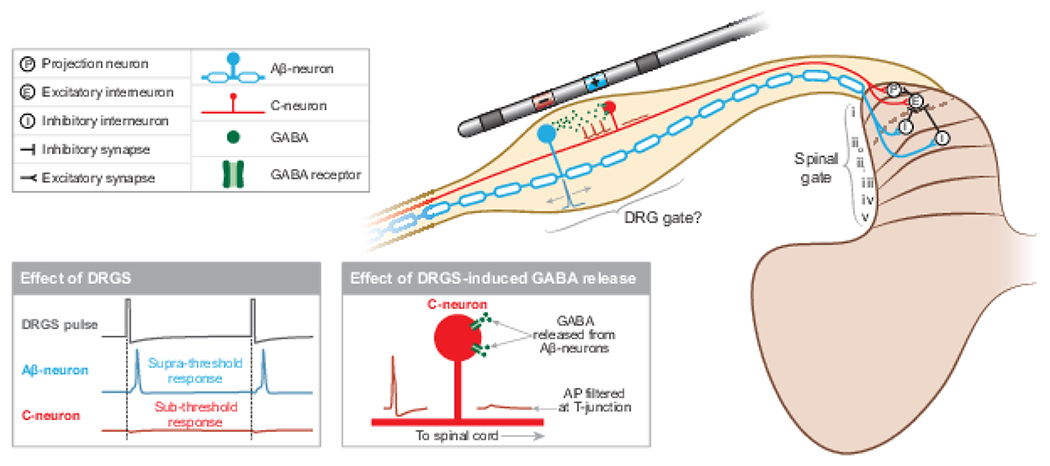
DRGS may drive pain-gating mechanisms in the spinal cord dorsal horn, the DRG, or both. DRGS applies trains of electrical pulses which induce APs in Aβ-neurons, which activate inhibitory interneurons in lamina iii and iii in the dorsal horn. Concurrently, Aβ-neurons may release GABA within the DRG, which can act on C-neurons and potentially prevent ectopic APs from propagating to the spinal cord.
