Figure 18. Interpenetrating network (IPN) biopolymer hydrogels.
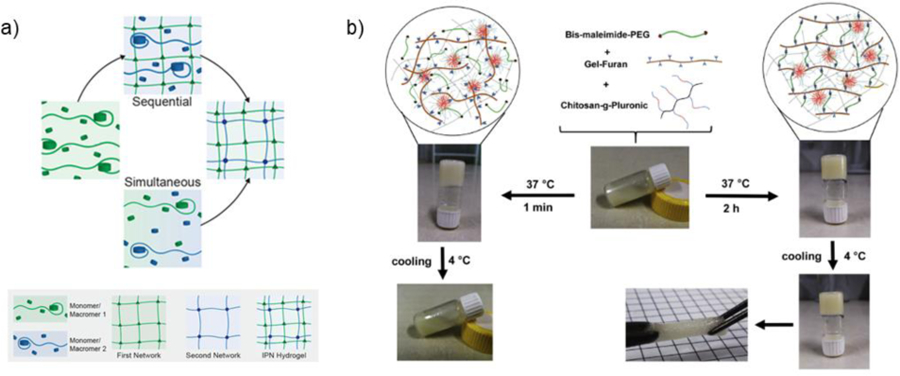
a) IPN hydrogels are formed through various synthesis techniques, including the sequential (swelling of first network in a secondary monomer/macromer) or simultaneous (orthogonal crosslinking of both first and second networks) introduction of networks. Adapted with permission from Dhand, et al.439 Copyright 2020, Elsevier. b) An IPN is formed by combining bis-maleimide-PEG, furan-modified gelatin (Gel-Furan), and chitosan grafted with Pluronic F127 (Chitosan-g-Pluronic). Initially, Chitosan-g-Pluronic formed a physically crosslinked, thermosensitive hydrogel network. After 2 h, Diels-Alder crosslinks between bis-maleimide-PEG and Gel-Furan covalently stabilize the hydrogel. Adapted with permission from Abandansari, et al.442 Copyright 2018, Elsevier.
