Figure 3. Crosslinking via free radical chain polymerization.
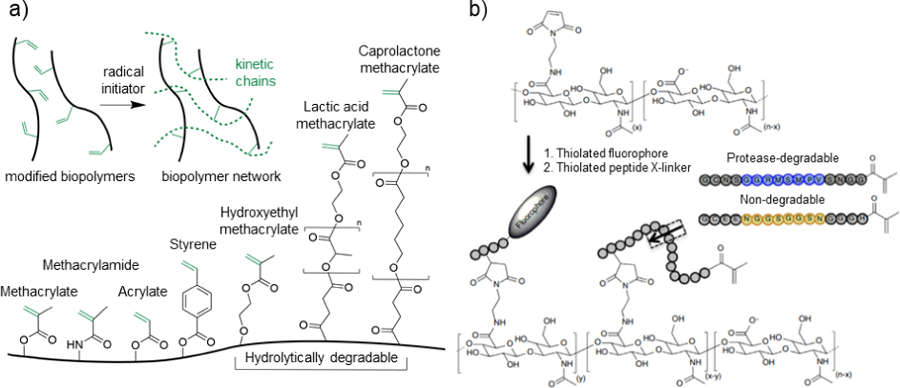
a) Schematic representation of the general crosslinking of modified biopolymers in the presence of an initiator to induce the formation of kinetic chains through the propagation of radical species (top), as well as common reactive groups used for biopolymer modification and hydrogel formation (bottom). b) Hyaluronic acid (HA) modified with maleimide groups to react with thiolated fluorophores and thiolated protease-degradable peptides capped with methacrylate groups for free radical chain polymerization. Peptide sequences are designed to be either protease degradable (blue) or non-degradable (yellow). Adapted with permission from Wade, et al.167 Copyright, 2015 Springer Nature.
