Yield, purity, and molar activity of [11C]HCN.
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Method | Routea | [11C]HCN | [11C]BnCNf | ||||
| Yield (%) | Purity (%) | Yield (%) | A m g (GBq μmol−1) | |||||
| EOBh | EOTi | EOSj | EOTi | EOSj | ||||
| 1 | Current | Route 1b | 60 ± 2.5 | 42 ± 1.6 | 94 ± 0.8 | 11 ± 1.4 | 349 ± 29 | 198 ± 18 |
| 2 | Current | Route 2c | 52 ± 4.1 | 37 ± 2.7 | 88 ± 1.6 | 9.5 ± 0.8 | 340 ± 62 | 193 ± 38 |
| 3 | Traditional | Route 3d | 51 ± 5.6 | 41 ± 4.8 | >99% | 11 ± 1.9 | 103 ± 69 | 53 ± 36 |
| 4 | Traditional | Route 4e | — | — | — | 7.8 ± 1.2 | 109 ± 35 | 55 ± 17 |
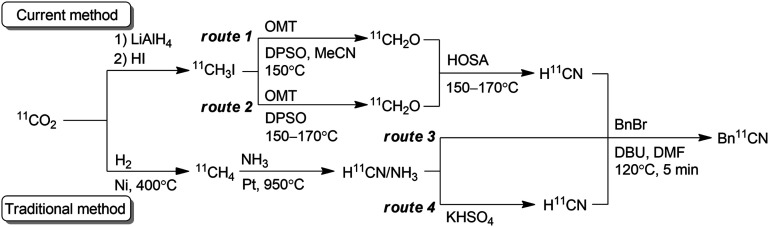
Values are presented as mean ± sd (n = 3). Synthetic route for the preparation of [11C]HCN.
The N-oxide layer of reaction column was prepared with the OMT solution.
A mixture of powdered OMT, DPSO, and SiO2 granules was used as the N-oxide layer.
Ordinary synthetic route for [11C]HCN preparation with NH3 included in the carrier gas of [11C]HCN (5% in N2).
NH3 in the carrier gas of [11C]HCN was removed (<0.2 ppm).
Reaction conditions: [11C]HCN was transferred to a reaction vessel containing a DMF solution (300 μL) of benzyl bromide (BnBr, 1 μL) and 1,8-diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene (DBU, 1 μL) at −20 °C until the radioactivity in the vessel reached a plateau. [11C]HCN was then reacted at 120 °C for 5 min.
Molar activity.
At the end of bombardment.
At the end of [11C]HCN transfer.
At the end of synthesis (purification).
