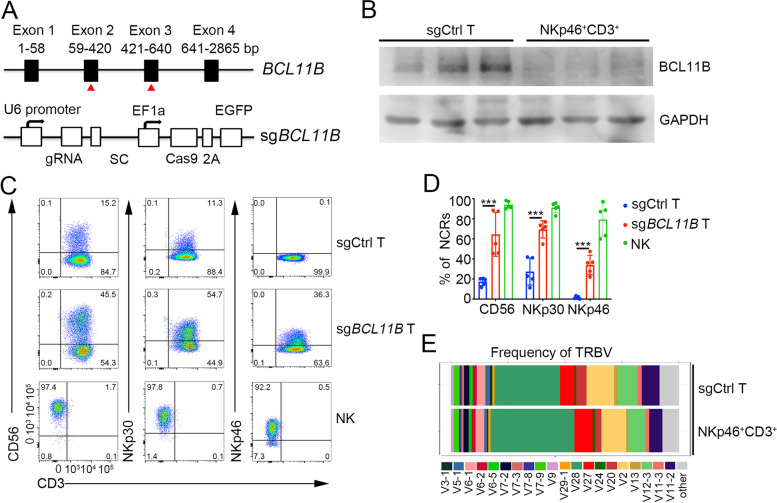
Fig. 1.
Reprogramming of primary human T cells into ITNKs by inactivating BCL11B. A sgRNA targeting exon 2 and exon 3 of the BCL11B locus. sgRNA, Cas9 and EGFP elements were integrated into a single vector. B Western blot analysis of BCL11B (120 kDa) levels in three representative samples of CB-derived T cells that were transduced with sgCtrl or NKp46+CD3+ cells (purity: 92.41 ± 2.60%) that were sorted from sgBCL11B-engineered T cells. C Representative flow cytometric detection of CD3, CD56, NKp30 and NKp46 in T cells: T cells transduced with sgCtrl, T cells transduced with sgBCL11B and normal NK cells (CD3−CD56+). Data are representative of five independent experiments. D Graph summarizing the percentages of CD56+, NKp30+, and NKp46+ cells in CD3+ T cells that received sgBCL11B or sgCtrl at 14 days post electroporation. The mean values of five independent healthy donors are shown. P < 0.001 for CD56+, NKp30+ and NKp46+ T cells in sgBCL11B-electroporated T cells compared to sgCtrl-electroporated T cells. ***P ≤ 0.001, two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test. E TCR diversity in sgCtrl T and NKp46+CD3+ cells purified from sgBCL11B-edited T cells from the same donor based on variable chain sequencing data for the TCRβ locus. The 20 variable chain sequences at the TCRβ locus were analyzed