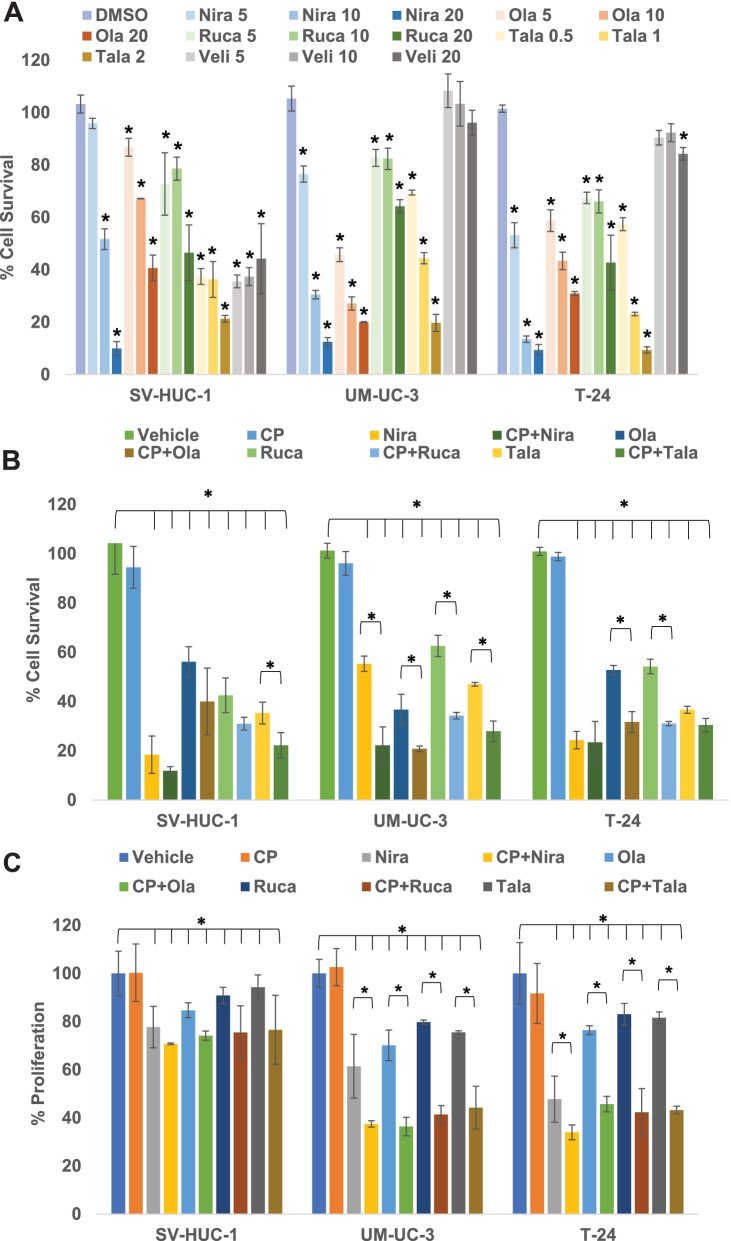
Fig. 2.
PARPi suppress the cell survival and proliferation of BLCA cells in vitro. A The BLCA cell lines UM-UC-3 and T-24 and the normal urothelial cells SV-HUC-1 were treated with varying concentrations of PARPi (niraparib, olaparib, rucaparib, talazoparib, or veliparib) for 72 h to determine the effective concentrations to be used in subsequent assays. Cell survival was measured as the percentage of cells surviving in comparison with the DMSO vehicle control in each cell line. B The BLCA cell lines UM-UC-3 and T-24 and the normal urothelial cells SV-HUC-1 were treated with sub-IC50 concentrations of niraparib, olaparib, rucaparib (5 μM each), talazoparib (0.5 μM) either singly or in combination with sub-IC50 concentration of cisplatin (0.5 μM) for 72 h. Cell survival was measured as the percentage of cells surviving in comparison with DMSO vehicle control in each cell line. C The BLCA cell lines UM-UC-3 and T-24 and the normal urothelial cells SV-HUC-1 were treated with sub-IC50 concentrations of niraparib, olaparib, rucaparib (5 μM each), talazoparib (0.5 μM) either singly or in combination with sub-IC50 concentration of cisplatin (0.5 μM) for 72 h. Cell proliferation was measured as the percentage of cells proliferating in comparison with DMSO vehicle control in each cell line. All results are presented as means±SD of 3 independent experiments with triplicates. P ≤ 0.05 was considered significant (*)