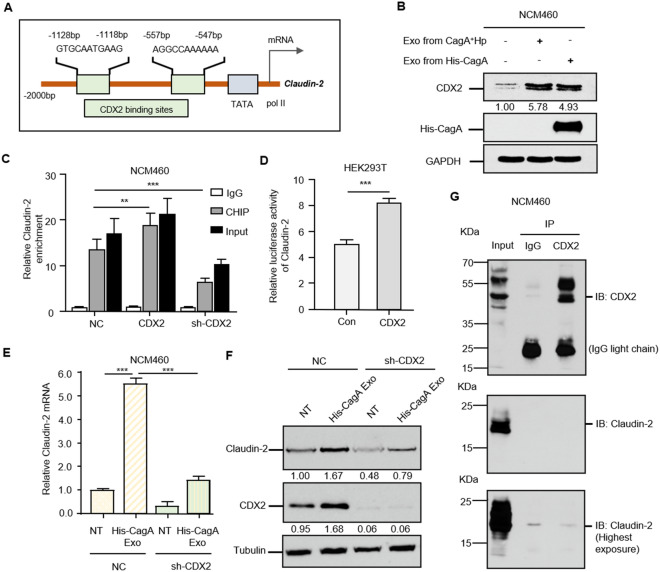
Fig. 3.
CagA activates CDX2 to transcriptionally upregulate Claudin-2 expression. A Schematic binding prediction of the transcription factor CDX2 in the Claudin-2 gene promoter. The two positions and sequences with relatively high scores are indicated. B Western blotting confirmed the incremental CDX2 protein expression by CagA. In addition to exosomes from GES-1 gastric epithelial cells cultured with CagA+ H. pylori, recombinant His-CagA protein was utilized to perform CagA and GES-1 cell cocluture and subsequent exosome isolation. Both exosomes from CagA+ H. pylori infection and recombinant CagA protein incubation triggered CDX2 expression. The presence of CagA in exosomes was proven using an antibody against the His-tag. Notably, the more striking contrast of the CDX2 band was shown above at shorter exposure times due to its abundant endogenous expression in the colon. C Identification of the CDX2-Claudin-2 interaction using chromatin immunoprecipitation. CDX2 interferences were introduced into NCM460 cell. CDX2 protein was able to pull down Claudin-2 DNA fragments. IgG and Input were performed as controls. D The positive transcriptional regulation of Claudin-2 by CDX2 was confirmed by luciferase reporter assay. The ratio of firefly luciferase activity to Renilla activity was calculated to show the binding of CDX2 to gene promoter activities. Each experiment was performed in triplicate. E, F CDX2 depletion impeded CagA-associated Claudin-2 transcription and protein expression. Data are presented as the mean ± SD value from three biological replicates. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, t test. G Coimmunoprecipitation precluded the protein interaction of CDX2 and Claudin-2. The equal CDX2 loading in the IP panel was preverified, and immunoblotting with Claudin-2 provided no binding of CDX2 and Claudin-2 even under the longest exposure