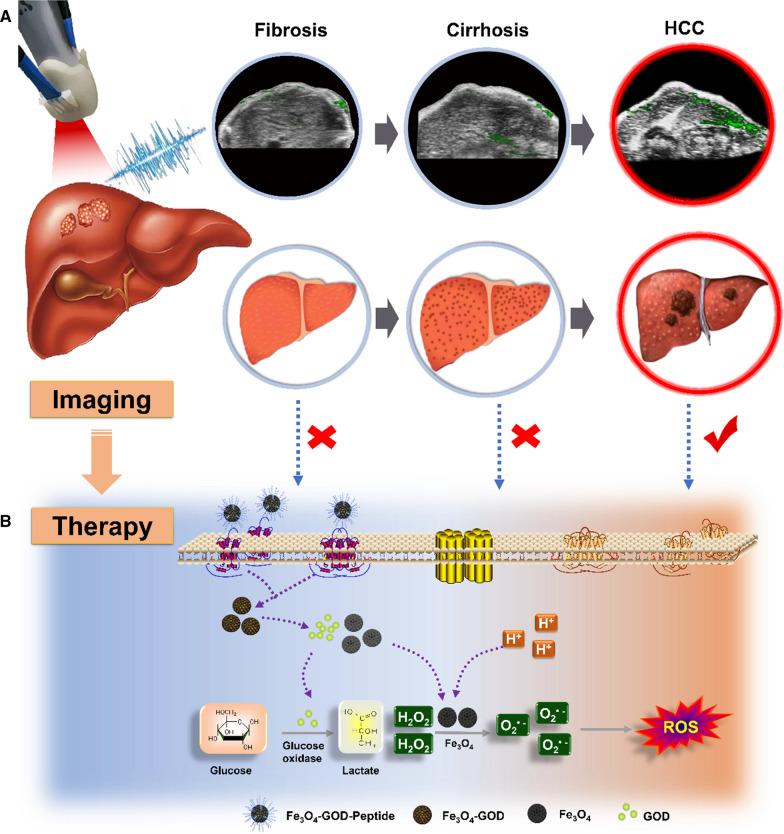
Scheme 1.
Scheme of targeted detection and sequential treatment of small hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in complex liver environment. A The development of liver cancer was simulated in vivo using CCl4 to induce the formation of liver cancer. Each stage (like fibrosis, cirrhosis and HCC) of this process was imaged by US/PAI after injecting HCC targeted nanoparticles (Fe3O4-GOD-Peptide, FGP NPs). HCC model had a markedly stronger PAI signal, with low or no signal in fibrosis and cirrhosis model as comparison. B After targeting to the GPC3 on the HCC cell membrane, the FGP NPs can only exert the maximum killing effect in the TME because it is mildly acidic and glucose-dependent. Glucose oxidase (GOD) can react with glucose in the tumor cells to produce high levels of H2O2 and then continue to react with Fe3O4 to produce toxic ROS-·OH radicals in acidic environments, such as extracellular and partial organelles (e.g., lysosomes), to trigger tumor cell apoptosis