Figure. CAD event incidence stratified by IL-6 signaling and CKD status.
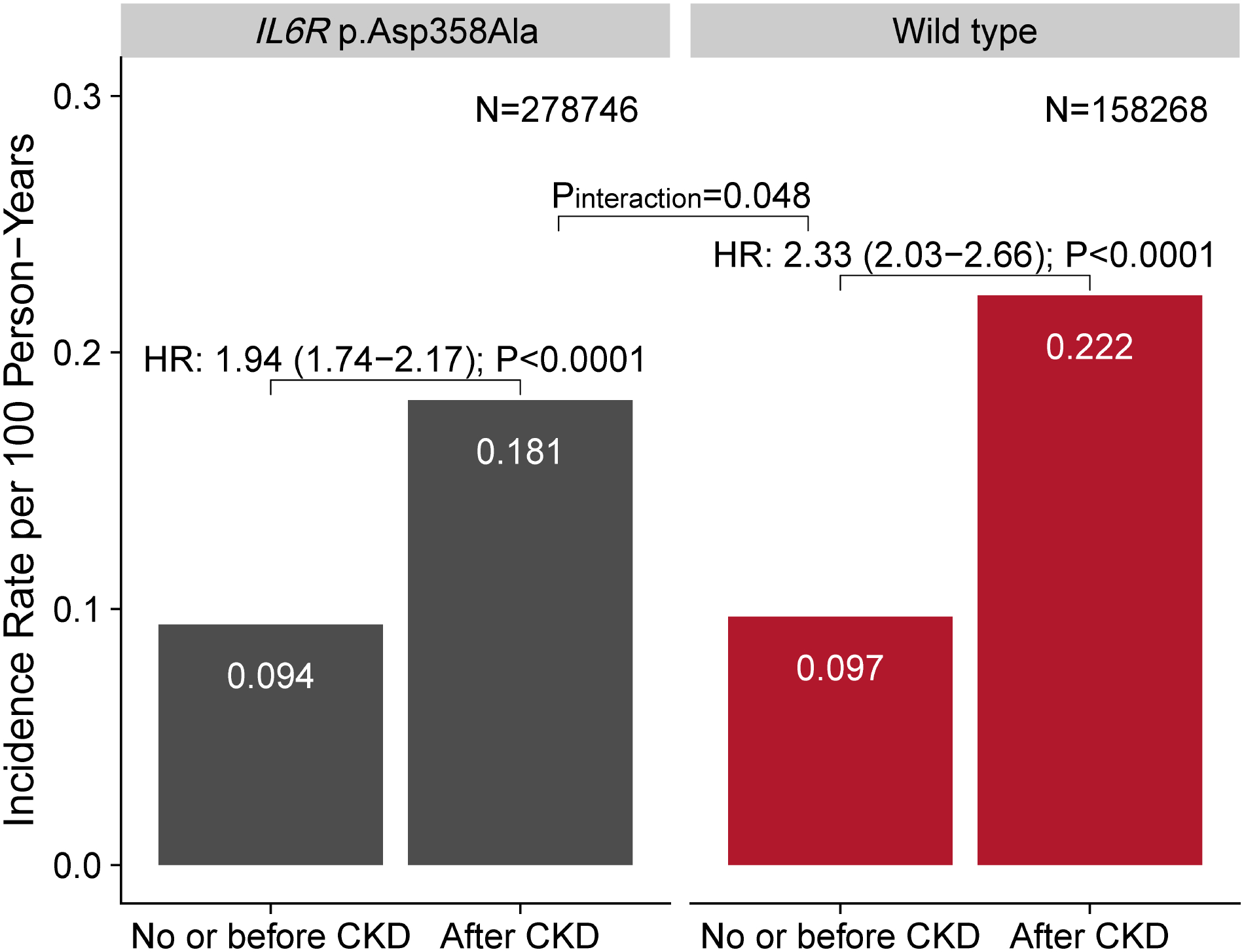
Incidence rates for CAD were adjusted for age categories, sex, race, baseline smoking status, and prevalent type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2D). CKD was associated with greater CAD risk among wild type [hazard ratio (HR): 2.33, 95% confidence interval (CI): 2.03 – 2.66] than IL6R p.Asp358Ala genotype (HR: 1.94, 95% CI: 1.74 – 2.17; Pinteraction = 0.048). HRs (95% CIs) of CKD were calculated from Cox proportional hazards models stratified by IL6R p.Asp358Ala carrier status. CKD status was modeled as a time-dependent covariate. Cox model was adjusted for age, sex, race, first 10 genetic principal components, baseline smoking status, prevalent T2D, and genotyping array. CAD: coronary artery disease; CKD: chronic kidney disease; IL-6: interleukin-6.
