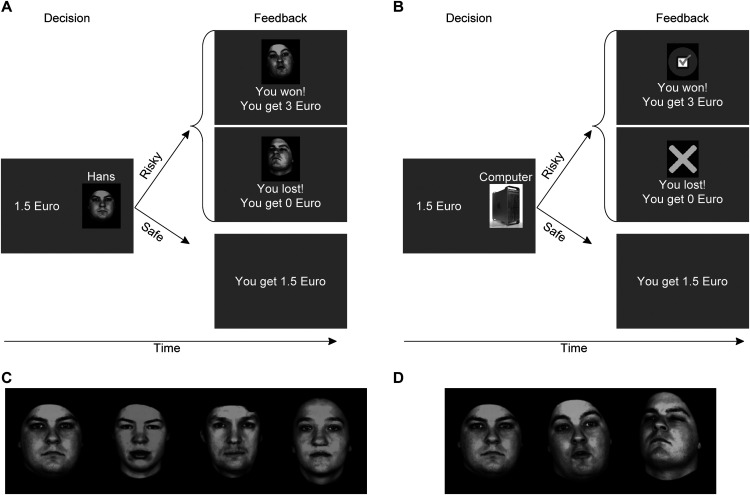
Figure 1.
Social gambling task. The social gambling task included a human (A) and a computer (B) condition, and each trial consisted of a decision and a feedback stage. During the decision phase, participants could choose a risky or a safe option (a uniformly distributed random fixed payoff ranging from 0 to 3 € in steps of 50 cents). If participants chose the risky option and won the trial, a positive feedback video of the partner was shown and the participant got 3 €. If participants lost the trial, they received no payoff and a negative feedback video was presented. The human feedback video displayed the virtual human partner expressing either admiration (participants won) or condescension (participant lost). In the computer control condition, the feedback was given by a video of a checkmark (participant won) or a cross (participant lost). If participants chose the safe option, a sentence confirmed the payoff. During fMRI, the partner was indicated by the name of the virtual human partner or the word “computer” only. C, The four virtual human partners with neutral facial expression. D, One of the partners with neutral, admiring, and condescending facial expressions (left to right). The admiring and condescending expressions were presented as videos during the feedback stage. See also Schultz et al. (2019, their Fig. 1).