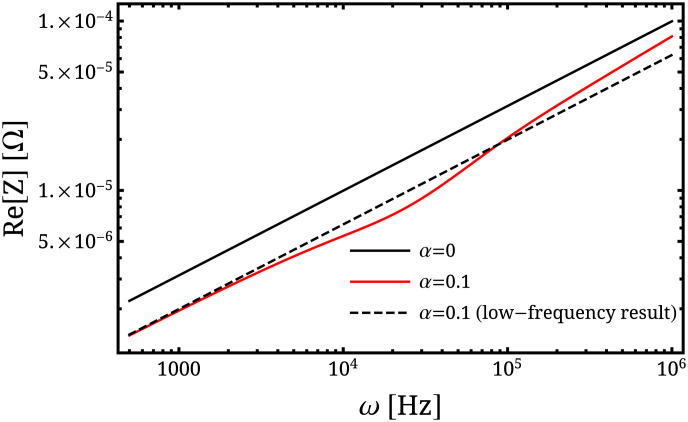
Fig. 4.
Dependence of the real part of the surface impedance Z on frequency ω in the low-frequency normal and the AIN regimes, obtained from Eqs. 53, 51, and 54 in the cases of no magnetic field (α = 0) and a nonzero magnetic field (). The dashed line is plotted on the basis of the impedance of the low-frequency normal regime as found in Table 1, and it is the result that would be measured in the absence of the nonlocal behavior. The material parameters are m/s, meV, Hz, and Hz. The transition to the AIN regime takes place around Hz. We see that changing the external magnetic field leads to a noticeable change of the surface impedance, especially shortly before the onset of the AIN regime, and moreover in this regime the scaling with frequency changes with respect to the no-field result.