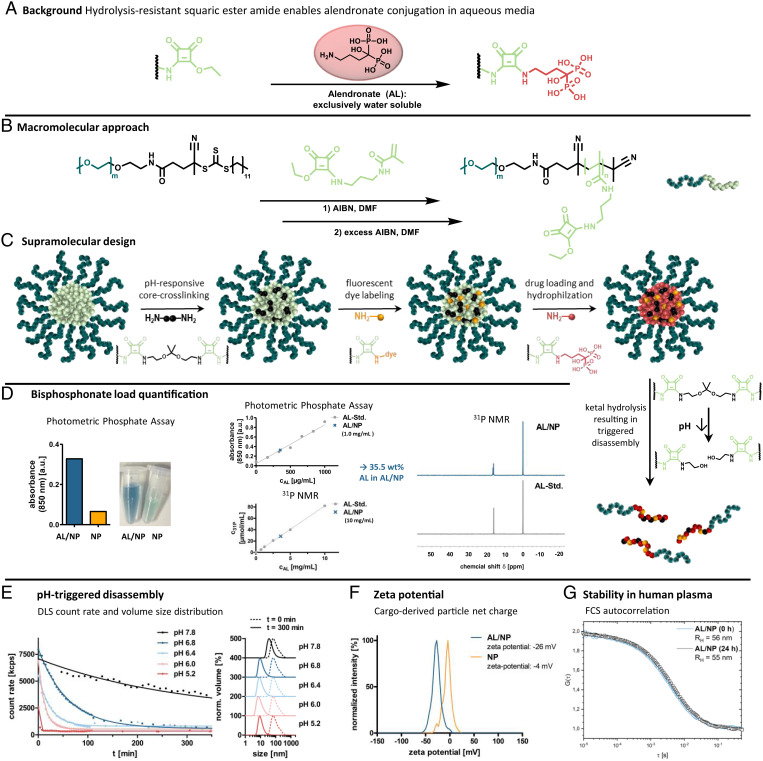
Fig. 1.
Nanocarrier fabrication and characterization. (A) Background: Covalent AL conjugation can be achieved by squaric ester amides under aqueous conditions. (B) Macromolecular approach: Synthesis scheme of RAFT block copolymerization of the squaric ester amide methacrylamide monomer with a PEG-derived chain transfer agent. (C) Supramolecular design: Scheme of nanogel fabrication from self-assembled squaric ester amide–based precursor micelles through sequential functionalization, including pH-responsive cross-linking, fluorescent dye labeling, and drug loading. Subsequent pH-triggered degradation can be afforded through acid-promoted hydrolysis of the ketal cross-linkers. (D) AL load quantification of AL/NPs using photometric phosphate assay and 31P NMR. (E) Ultrasensitive pH-triggered disassembly: DLS count rate of AL/NPs upon exposure to pH 7.8 compared to mildly acidic values of pH 6.8, 6.4, 6.0, and 5.2 over time. DLS size distribution of AL/NPs before (0 min, dotted line), as well as upon, exposure to the different pH values (300 min, solid line). (F) Zeta potential of bisphosphonate-loaded AL/NPs compared to control NPs. (G) Stability in human plasma: FCS study of AL/NPs after 0 and 24 h of incubation in human blood plasma. RH, hydrodynamic radii.