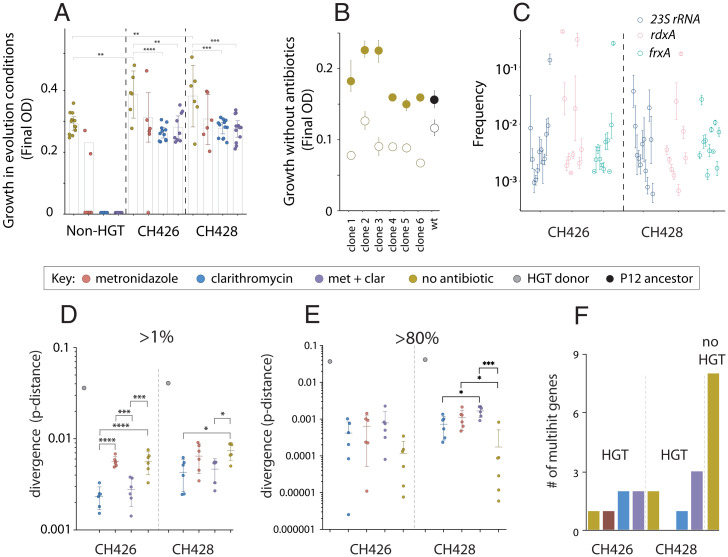
Fig. 2.
HGT increases the rate of phenotypic and molecular evolution. The maximum carrying capacity of each evolved population after 192 generations, measured in the same growth conditions as the evolution experiment. For example, the non-HGT treatment populations evolved and were measured in media without antibiotic (gold circles), while the non-HGT populations evolved in metronidazole were measured in media containing metronidazole (red circles). The non-HGT clarithromycin (blue circles)- and double-drug (purple circles)-treated populations went extinct and could not be measured (A). Growth experiments were carried out in media without clarithromycin to measure the cost of mutations in the 23S rRNA gene (B). The wild-type (black filled circle) and evolved clones (gold filled circles) were engineered with the A2143G substitution in 23S rRNA, that confers resistance to clarithromycin (open circles). The average frequency of variants in genes known to cause resistance to clarithromycin (23S rRNA), and metronidazole (rdxA and frxA) in populations that had evolved with HGT but in media without antibiotic, after 192 generations of evolution (C). The core genome dissimilarity (pairwise nucleotide p-distance) between the donor strains (CH426 and CH428) and the H. pylori P12 recipient strain (gray circles), and core genome dissimilarity between individual evolved populations and the H. pylori P12 recipient strain. In the case of the evolved populations, dissimilarity was calculated based on the number of variants that attained a frequency >1% or higher (D) or >80% (E). The number of multihit genes that evolved de novo mutations in parallel more often than expected in the six sequenced populations from each treatment (F). The no-HGT treatment populations evolved significantly more multihit genes by de novo mutation than the HGT treatment populations (one-sample Z test, z = 3.83, P = 6E−5). Asterisks indicate significance by Tukey's multiple comparison test: *P≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.