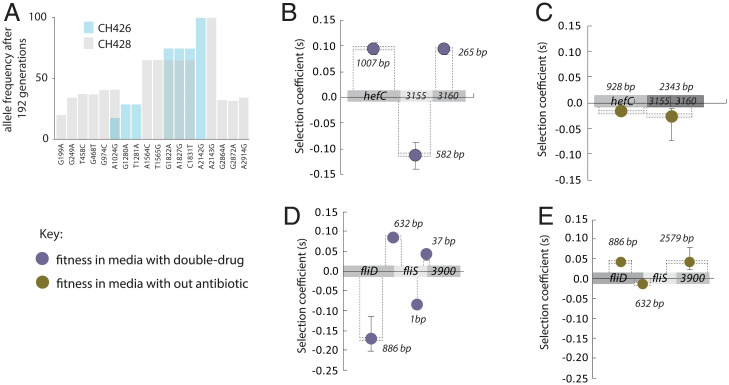
Fig. 6.
Recombination and selection. The frequency of HGT alleles in the 23s rRNA gene after 192 generations of selection in clarithromycin (A). The average frequency for horizontally transferred 23S rRNA gene variants in clarithromycin HGT treatment populations with the CH426 donor (blue bars) and the CH428 donor (gray bars). A single substitution in the 23S rRNA gene is sufficient for clarithromycin resistance and was fixed in conditions with clarithromycin (CH426 = A2142G; CH428 = A2143G). Each bar shows the mean of six populations. The frequencies of the other 23S rRNA alleles are negatively correlated with genetic distance to the fixed mutation (Pearson’s correlation coefficient, CH426, R = −0.98, P < 0.0001; CH428, R = −0.75, P = 0.0021). The fitness effects of HGT blocks in multihit genes measured in two environments, growth media with clarithromycin and metronidazole (purple circles B and D) and growth media without antibiotics (gold circles, C and E). The size of the selected blocks is indicated by the number of bases shown, and dashed lines show the approximate position of the blocks on the genes. For example, B shows that in the double-drug conditions, the 582-bp fragment is deleterious, while the 265-bp fragment is beneficial. However, in no-antibiotic conditions these two blocks segregate together as a weakly deleterious block. R is Pearson’s correlation coefficient.