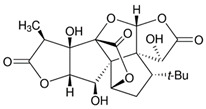
Ginkgolide A
(terpenoid)
|
Leaves, root, and bark. |
|
-
-
Anti-inflammatory (decreasing TNF-α, IL-1β, and NF-kB expression);
-
-
Antioxidant (reducing ROS and augmenting free radical capture by the cells);
-
-
Anxiolytic-like effects;
-
-
Neuroprotection (controlling neurodegeneration and inflammation);
-
-
Anti-atherosclerotic (prevention of OS to the endothelial cells/stimulation of NO);
-
-
Anti-thrombotic (inhibition of platelet aggregation by MMP-9 and controlling cAMP, inhibiting intracellular Ca2+ mobilization, and decreasing TXA2 activity);
-
-
Hepatoprotective (suppressing hepatocyte lipogenesis);
-
-
Antitumor (inhibition of cancer cell proliferation).
|
[12,42,43,44] |
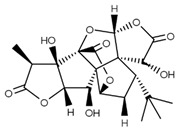
Ginkgolide B
(terpenoid)
|
Leaves, root, and bark. |
|
-
-
Neuroprotective effects (protecting neurons from βA apoptotic events and in ischemia/reperfusion syndrome through the regulation of NF-kB pathways);
-
-
Anti-inflammatory (decreasing TNF-α, IL-1β, and NF-kB expressions);
-
-
Antioxidant (reducing ROS and augmenting free radical capture);
-
-
Protective effects of cardiomyocytes against ischemia/reperfusion syndrome;
-
-
Inhibition of cancer cell migration and invasion;
-
-
Induction of cancer cell apoptosis.
|
[12,43,45,46,47,48,49,50,51] |
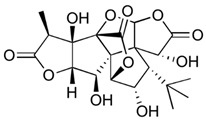
Ginkgolide C
(terpenoids)
|
Leaves, root, and bark. |
|
-
-
Anti-inflammatory (decrease in TNF-α, IL-1β, and NF-kB expression);
-
-
Antioxidant (reduces ROS and augments free radical capture);
-
-
Suppressor of adipogenesis via AMPK signaling pathways;
-
-
Hepatoprotective by protecting liver from lipid accumulation injuries;
-
-
Alleviation of ischemia/reperfusion syndrome in cardiomyocytes;
-
-
Antitumor effects (cancer cells apoptosis and inhibition of cancer cell growth).
|
[12,43,52,53,54,55,56] |
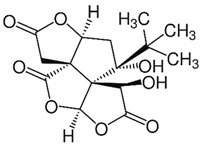
Bilobalide
(terpenoid)
|
Leaves and bark. |
|
-
-
Anti-inflammatory (decrease in TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 levels);
-
-
Neuroprotective (reduction in neuroinflammation and protection against βA deposition in AD);
-
-
Hepatoprotective;
-
-
Antioxidant via multiple pathways;
-
-
Cardioprotective.
|
[12,43,57,58,59] |
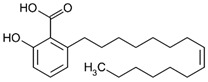
Ginkgolic acid
(organic acid)
|
Leaves. |
|
|
[43,60,61,62] |
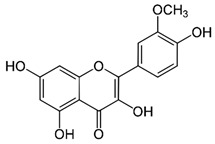
Isorhamnetin
(flavonoid)
|
Leaves. |
|
-
-
Anti-atherosclerosis and endothelium protective;
-
-
Neuroprotection (improvement of brain function and cognition);
-
-
Hypotensive effects;
-
-
Anti-ischemia and anti-fibrosis in myocardium;
-
-
Anti-inflammatory/antioxidant,
-
-
Antitumor effects (suppression of cancer growth and invasiveness).
|
[43,63,64,65,66,67] |
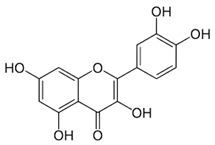
Quercetin
(flavonoid)
|
Leaves. |
|
-
-
Anti-inflammatory/antioxidant (decrease in lipid peroxidation and OS);
-
-
Increase in BDNF;
-
-
Reduces the degradation of serotonin by monoamine oxidases;
-
-
Antitumor (modulation of VEGF, P13K/Akt, apoptosis, mTOR, MAPK/ERK1-2, and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways);
-
-
Attenuation of atherosclerotic inflammation;
-
-
Cardioprotection (protection against OS/improvement of cardiomyocytes);
-
-
Antimicrobial.
|
[43,67,68,69,70,71,72,73] |
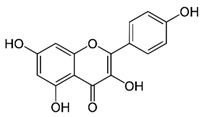
Kaempferol
(flavonoid)
|
Leaves. |
|
-
-
Antitumor (inhibiting cancer cell proliferation and stimulating apoptosis);
-
-
Antioxidant (upregulation of GSH);
-
-
Anti-inflammatory (inhibiting NF-kB, COX-2, and iNOS expression);
-
-
Neuroprotection (suppression of oxidative and inflammatory damage to brain cells);
-
-
Protection against ischemia/reperfusion syndrome and myocardial injury;
-
-
Upregulation of BDNF;
-
-
Reduction of serotonin degradation.
|
[12,43,74,75,76,77,78] |
Luteolin
(flavonoid)
|
Leaves. |
|
-
-
Anti-inflammatory (suppressing TNF-α, IL-6, COX-2, and NF-kB expressions);
-
-
Antioxidant;
-
-
Antitumor (inhibiting cancer cell proliferation and stimulating cell cycle arrest and apoptosis);
-
-
Neuroprotective (limiting βA deposition, reducing neuroinflammation and brain OS);
-
-
Cardioprotective effects (stimulation of cardiomyocyte function through MAPKs);
-
-
Reduction of cardiomyocyte ischemic/reperfusion syndrome.
|
[43,79,80,81] |









