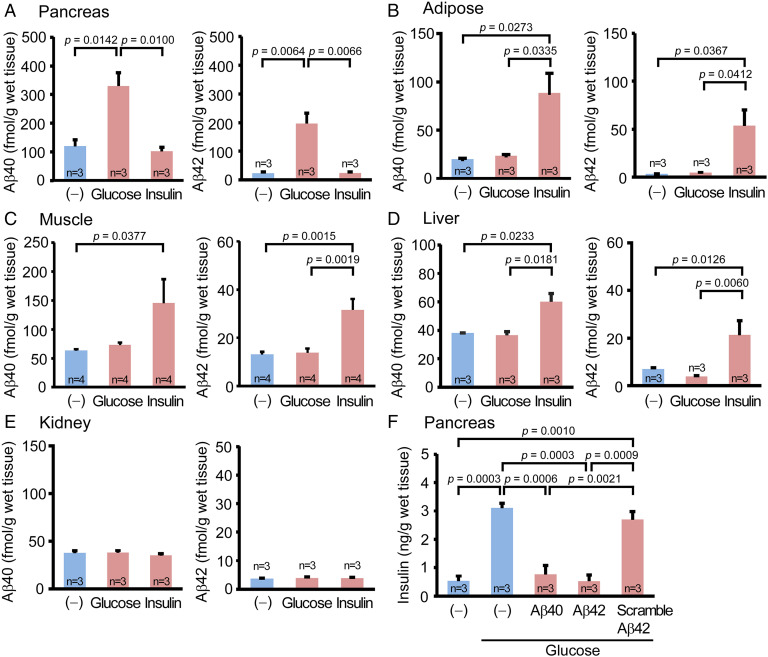
Fig. 2.
Ex vivo effects of glucose and insulin loading on Aβ secretion and of Aβ loading on insulin secretion in live peripheral tissues isolated from mice. The pancreas (A), abdominal white adipose tissues (B), anterior tibial muscles (C), liver (D), and kidneys (E) were collected from fasted wild-type mice. The minced tissues were stimulated with high-glucose or insulin for 60 min. High-glucose stimulation significantly increased Aβ40 and Aβ42 secretion from the pancreatic tissues, but not the adipose, muscle, or liver tissues. In contrast, insulin stimulation significantly enhanced Aβ40 and Aβ42 secretion from the adipose, muscle, and liver tissues but not the pancreatic tissues. In either condition, Aβ secretion was not detected from the kidney tissues. (F) The pancreatic tissues were stimulated with high-glucose with or without Aβ40, Aβ42, or scramble Aβ42 peptide for 60 min. Glucose-induced insulin secretion was significantly attenuated in the presence of Aβ40 and Aβ42 but not of scramble Aβ42 peptide.