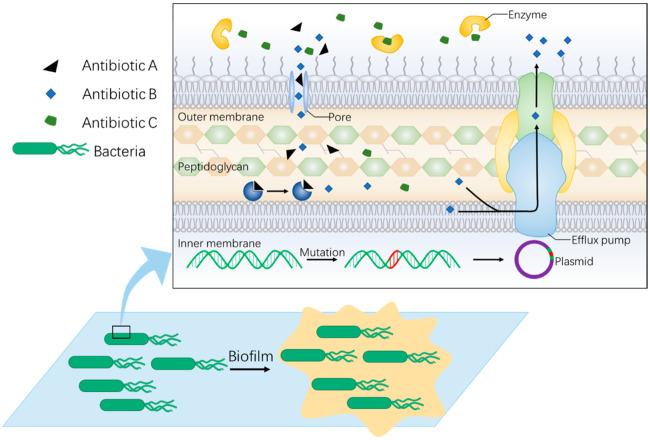
Figure 1.
Mechanisms of bacterial resistance. The figure shows a brief overview of intrinsic resistance mechanisms. Firstly, bacteria acquire drug-resistance through gene mutation at the genetic level. The mutated gene can also spread through vertical and horizontal transmission (herein, plasmid for example). Besides, biochemical mechanisms are a more common style of antidrug upon target change, efflux or inactivation. Moreover, the formation of biofilm prevents bacteria from reaching the antibiotic and enhances drug resistance.